Ahmad Adi, MD
- Department of Cardiothoracic Anesthesiology
- Cleveland Clinic
- Cleveland, Ohio
Return to 1319 nm Applications screen softkey the Return to 1319 nm Applications softkey will return the system to the previous screen erectile dysfunction depression treatment order genuine nizagara on line. Either the paddle chill plate or the single spot chill plate can be used for the treatment erectile dysfunction implant cheap nizagara online amex. This enables the Pro-V to treat veins without contact of the vein wall erectile dysfunction treatment japan cheap nizagara, minimizing the risk of bruising candida causes erectile dysfunction generic nizagara 50 mg overnight delivery, discomfort do herbal erectile dysfunction pills work purchase 100mg nizagara overnight delivery, and perforation of veins erectile dysfunction 60 generic nizagara 25mg. Rate indicator Rate indicator displays the repetition rate at which the energy is being delivered and is measured in Hz. Energy adjustment softkeys Energy adjustment softkeys allow the user to increase or decrease energy by 0. Average power indicator Average power indicator shows the amount of power being delivered in Watts. Accumulated Data indicator Accumulated Data displays the total energy being delivered in Joules and the total time of the treatment in seconds. Return to Fiber Applications screen Return to Fiber Applications softkey will return the system to the previous screen. Veins return blood from the rest of your body to your heart, so the blood can be recirculated. Muscle contractions in the lower legs act as pumps, and elastic vein walls help blood return to the heart. Tiny valves in the veins open as blood flows toward the heart then close to stop blood from flowing backward. The valves in the veins may become weak, allowing blood that should be moving toward your heart to flow backward. Pregnancy increases the volume of blood in the body, but decreases the flow of blood from the legs to your pelvis. This circulatory change is designed to support the growing fetus, but it can produce an unfortunate side effect enlarged veins in the legs. Varicose veins may surface for the first time or may worsen during late pregnancy, when the uterus exerts greater pressure on the veins in the legs. Varicose veins that develop during pregnancy generally improve without medical treatment within three months after delivery. Sciton recommends that each user attend a Preceptor training course prior to offering Pro-V procedures to their patients. After sterile prepping and draping of the leg, the ultrasound probe is placed into a sterile probe cover. Wear safety glasses appropriate for 1319 nm; patient as well as all staff in treatment room. Laser fibers are inherently fragile and so care should be exercised in handling them. Confirm the laser fiber tip position using ultrasound and pull the introducer sheath out of the vein, leaving only the proximal tip in the skin edge. Intravascular burning of the sheath by the laser beam may damage the sheath and/or cause a patient reaction. Observe tissue response on ultrasound for the following: fi Slowing or stopping of forward movement of flow. Make sure that the pull-back device is positioned so that the arrows indicate the correct direction of the fiber movement. Insert the fiber into the pull-back device, ensuring that the fiber is positioned over the roller wheel. Inserting Fiber into Pull-Back Device Stop the pull-back device if laser treatment is interrupted to avoid untreated segments of the vein. Do not continue laser treatment unless the aiming beam is present and fiber movement is confirmed. Place fingers on either side of the fiber at the exit point from the skin to verify movement and to support the fiber as it is being pulled out. When the fiber is a few centimeters from the access site, stop laser treatment and turn off the pull-back device. Remove the introducer sheath completely from the vein and resume laser treatment with a manual pull back of the fiber until the fiber exits the vein. Following the treatment, observe the appearance of the vein with the ultrasound: fi Vein appears more dense and thickened (more echogenic) fi Vein is less compressible with pressure from the ultrasound probe fi Vein lumen is noticeably smaller in size fi Vein does not demonstrate spontaneous flow 21. Document laser treatment parameters including: fi Fiber size, Watts and Hz fi Pull-back speed and treatment length. This combination allows for fractionated non-ablative and ablative skin resurfacing resulting in a cosmetic improvement in pigmentation, tone and texture of skin as well as other effects of photoaging. Daily use of sun block immediately after treatment, and for at least the next 30 days, is recommended to avoid pigment related complications. The residual heat could lead to undesirable pigment related issues in darker skin types. The epidermis of the neck, chest, hands, and general body surfaces is thinner than that of the face and has fewer adnexal healing structures. Depth of Penetration Depth of penetration of laser energy for different types of lasers is seen illustrated. This creates microscopic columns of wounded tissue that stimulate neocollagenesis, a process in which new collagen is produced by the body. The sequential use of 2940 nm wavelength selectively targets epidermis containing water and hemoglobin to precisely vaporize (ablate) tissue in a controlled manner. Initially, all Asian skins should be treated as a Skin Type V until reaction to laser light has been determined. Similarly, not all black skins are of the same degree of darkness and there may be the temptation to type these patients as a lower type. Corticosteroid therapy may be considered to reduce significant post treatment swelling. Remove before treatment with mild soap and water or an alcohol swab, then plain water. Be extremely cautious when applying topical anesthetics to large areas of the body. A smoke evacuator should be used at all times when smoke is created in order to collect the plume. The other end is secured to the adapter to fit snuggly on the smoke evacuator (see photo in treatment basics). Before treatment, with the Zimmer chiller unit, test adequate smoke evacuation and chilled airflow. These wounds stimulate neocollagenesis and help to reduce the signs of photoaging. Pressing this softkey brings user to the data 2 entry screen for entering the length and width for these zones in cm. Fixed treatment area measure softkey Pressing this softkey brings the user to the data entry screen for entering the length and width for the fixed zone. Target energy display Based upon the Target % coverage selected, the target energy to be delivered is displayed here. Treatment Summary softkey Touching this softkey permits the user to enter the Treatment Summary screen where the treatment area, target/delivered energy and 1470 depth/coverage are displayed for the five treatment zones. Adapter Life Time indicator the indicator displays the time of use of the disposable adapter. When increasing the density pay careful attention to patient skin types and/or history of pigmentary issues such as hyper or hypo pigmentation. Mapping return softkey Touching this softkey will return the user to the 1470nm/2940nm applications screen. Face treatment area zone measure softkey There are five facial zones that comprise the treatment area. Area (cm) indicator 2 For each measured zone, area is populated in this box in cm. Velocity Meter Provides visual feedback on correct velocity of handpiece movement. Treatment Summary softkey Touching this softkey permits the user to enter the Treatment Summary screen where the treatment area, target/delivered energy, 1470 depth/coverage and 2940 depth/coverage are displayed for the five treatment zones. Set Parameters Depth (um) / Coverage (%) softkey Touching this softkey permits the user to enter the Depth (um) / Coverage or Density (%) screen where depth of treatment and the percent coverage can be selected. Density setting softkey Touching this softkey using either the back or forward arrow adjusts the level of density delivered. Please consult with your medical director if you have specific treatment questions. Mapping Return softkey Touching this softkey will return the user to the to 1470nm/2940nm Applications screen. Before beginning treatment, ensure that topical has been completely removed from the skin surface. The position should be comfortable to the patient and such that the treatment provider has good access to area to be treated and the control panel display screen. Only one side of each area needs to be measured and the system auto populates the opposite side with the same measurement and assumes symmetry. If choosing a fixed area, press the Area softkey to enter the fixed area measuring screen as seen below right. Face area measuring data screen Fixed area measuring data screen fi Select length or width softkey for desired direction. These two measurements 2 will be calculated to give the total area measurement in cm and will be shown in the area box. Treatment Parameters fi Enter appropriate settings into the control panel display screen based on condition and area to be treated. An audible tone will be heard when the calculated joules has been reached to indicate completion. This unique thermal sensor constantly monitors the epidermal skin temperature before each pulse to optimize the fluence and spot size ensuring the exact depth entered on the screen. To navigate the zone being treated, gently roll the scanner starting in a single pass technique. Next repeat process until this treatment zone has been treated with 2 vertical passes 4. Next repeat process until this treatment zone has been treated with 2 horizontal passes 7. The energy will be deposited and a sound will let the user know that the recommended total energy has been completed. The horizontal bar on the Percent (%) Coverage will be completely filled to indicate that that the Accumulated % Coverage has reached the Target % Coverage. The redness and healing (often similar in appearance to varying degrees of sunburn) will increase with the ablation depth and coverage, and will vary by patient. The 1470 nm wavelength is absorbed by water making it ideal for heating of soft tissue to create controlled zones of coagulation to chosen depths into the vaginal mucosa. This combination allows for fractionated non-ablative and ablative resurfacing for an improvement to vaginal tissue. Arm Application Menu Screen the Arm Application menu screen allows the user to enter diVa application screen. Arm Applications Softkey Touching the 1470/2940 softkey will allow the user to access the 1470/2940 applications. Return to Arm Applications screen softkey Touching this key will return the system to the previous screen 9. Prednisone, Dexamethasone) fi Patients who are pregnant or lactating fi Patients who have used isotretinoin. The potential complications of diVa are: fi Scarring, hypertrophic and non-hypertrophic fi Burn, from superficial to full thickness fi Extensive tissue destruction fi Ulceration fi Induced bruising or petechiae formation fi Severe edema 9. It does not cause the water in the tissue to vaporize (ablate) but rather the laser energy heats the tissue in a controlled manner. The coincident and independent use of 2940 nm wavelength selectively targets the mucosal epithelial layer containing water and hemoglobin to precisely vaporize (ablate) tissue in a controlled manner. It is recommended that a brief medical history be taken before beginning any subsequent treatment by reviewing clinical information such as any new medications, pertinent change from last treatment, pregnancy etc. Each patient should be assessed and questioned regarding allergies or sensitivities to ingredients in topical anesthetics prior to application. During the first day after a treatment, new mucosal epithelial cells proliferate underneath the necrotic tissue. The mucosal epithelial layer tissue responds immediately to the initial ablative process allowing for quicker healing and minimal downtime.
Diagnostic guidelines Although the most typical form of bipolar disorder consists of alternating manic and depressive episodes separated by periods of normal mood new erectile dysfunction drugs 2012 nizagara 100mg otc, it is not uncommon for depressive mood to be accompanied for days or weeks on end by overactivity and pressure of speech erectile dysfunction zoloft generic nizagara 25 mg without a prescription, or for a manic mood and grandiosity to be accompanied by agitation and loss of energy and libido erectile dysfunction korean ginseng buy nizagara mastercard. Depressive symptoms and symptoms of hypomania or mania may also alternate rapidly health erectile dysfunction causes purchase 100mg nizagara, from day to day or even from hour to hour youth erectile dysfunction treatment purchase nizagara 25 mg overnight delivery. A diagnosis of mixed bipolar affective disorder should be made only if the two sets of symptoms are both prominent for the greater part of the current episode of illness treatment erectile dysfunction faqs buy nizagara with mastercard, and if that episode has lasted for at least 2 weeks. The patient may, however, be receiving treatment to reduce the risk of future episodes. Other common symptoms are: (a)reduced concentration and attention; (b)reduced self-esteem and self-confidence; (c)ideas of guilt and unworthiness (even in a mild type of episode); (d)bleak and pessimistic views of the future; (e)ideas or acts of self-harm or suicide; (f)disturbed sleep (g)diminished appetite. The lowered mood varies little from day to day, and is often unresponsive to circumstances, yet may show a characteristic diurnal variation as the day goes on. As with manic episodes, the clinical presentation shows marked individual variations, and atypical presentations are particularly common in adolescence. In some cases, anxiety, distress, and motor agitation may be more prominent at times than the depression, and the mood change may also be masked by added features such as irritability, excessive consumption of alcohol, histrionic behaviour, and exacerbation of pre-existing phobic or obsessional symptoms, or by hypochondriacal preoccupations. For depressive episodes of all three grades of severity, a duration of at least 2 weeks is usually required for diagnosis, but shorter periods may be reasonable if symptoms are unusually severe and of rapid onset. Some of the above symptoms may be marked and develop characteristic features that are widely regarded as having special clinical significance. The most typical examples of these "somatic" symptoms (see introduction to this block, page 112 [of Blue Book]) are: loss of interest or pleasure in activities that are normally enjoyable; lack of emotional reactivity to normally pleasurable surroundings and events; waking in the morning 2 hours or more before the usual time; depression worse in the morning; objective evidence of definite psychomotor retardation or agitation (remarked on or reported by other people); marked loss of appetite; weight loss (often defined as 5% or more of body weight in the past month); marked loss of libido. Usually, this somatic syndrome is not regarded as present unless about four of these symptoms are definitely present. Further depressive episodes should be classified under one of the subdivisions of recurrent depressive disorder (F33. These grades of severity are specified to cover a wide range of clinical states that are encountered in different types of psychiatric practice. Individuals with mild depressive episodes are common in primary care and general medical settings, whereas psychiatric inpatient units deal largely with patients suffering from the severe grades. These codes do not involve differentiation between attempted suicide and "parasuicide", since both are included in the general category of self-harm. Differentiation between mild, moderate, and severe depressive episodes rests upon a complicated clinical judgement that involves the number, type, and severity of symptoms present. The extent of ordinary social and work activities is often a useful general guide to the likely degree of severity of the episode, but individual, social, and cultural influences that disrupt a smooth relationship between severity of symptoms and social performance are sufficiently common and powerful to make it unwise to include social performance amongst the essential criteria of severity. The presence of dementia (F00-F03) or mental retardation (F70-F79) does not rule out the diagnosis of a treatable depressive episode, but communication difficulties are likely to make it necessary to rely more than usual for the diagnosis upon objectively observed somatic symptoms, such as psychomotor retardation, loss of appetite and weight, and sleep disturbance. Includes: single episodes of depressive reaction, major depression (without psychotic symptoms), psychogenic depression or reactive depression (F32. An individual with a mild depressive episode is usually distressed by the symptoms and has some difficulty in continuing with ordinary work and social activities, but will probably not cease to function completely. A fifth character may be used to specify the presence of the somatic syndrome: F32. Several symptoms are likely to be present to a marked degree, but this is not essential if a particularly wide variety of symptoms is present overall. An individual with a moderately severe depressive episode will usually have considerable difficulty in continuing with social, work or domestic activities. A fifth character may be used to specify the occurrence of the somatic syndrome: F32. Loss of self-esteem or feelings of uselessness or guilt are likely to be prominent, and suicide is a distinct danger in particularly severe cases. It is presumed here that the somatic syndrome will almost always be present in a severe depressive episode. Diagnostic guidelines All three of the typical symptoms noted for mild and moderate depressive episodes (F32. However, if important symptoms such as agitation or retardation are marked, the patient may be unwilling or unable to describe many symptoms in detail. The depressive episode should usually last at least 2 weeks, but if the symptoms are particularly severe and of very rapid onset, it may be justified to make this diagnosis after less than 2 weeks. During a severe depressive episode it is very unlikely that the sufferer will be able to continue with social, work, or domestic activities, except to a very limited extent. This category should be used only for single episodes of severe depression without psychotic symptoms; for further episodes, a subcategory of recurrent depressive disorder (F33. The delusions usually involve ideas of sin, poverty, or imminent disasters, responsibility for which may be assumed by the patient. Auditory or olfactory hallucinations are usually of defamatory or accusatory voices or of rotting filth or decomposing flesh. If required, delusions or hallucinations may be specified as mood-congruent or mood-incongruent (see F30. This category should be used only for single episodes of severe depression with psychotic symptoms; for further episodes a subcategory of recurrent depressive disorder (F33. Includes: single episodes of major depression with psychotic symptoms, psychotic depression, psychogenic depressive psychosis, reactive depressive psychosis F32. Examples include fluctuating mixtures of depressive symptoms (particularly the somatic variety) with non-diagnostic symptoms such as tension, worry, and distress, and mixtures of somatic depressive symptoms with persistent pain or fatigue not due to organic causes (as sometimes seen in general hospital services). However, the category should still be used if -103 there is evidence of brief episodes of mild mood elevation and overactivity which fulfil the criteria of hypomania (F30. The age of onset and the severity, duration, and frequency of the episodes of depression are all highly variable. In general, the first episode occurs later than in bipolar disorder, with a mean age of onset in the fifth decade. Individual episodes also last between 3 and 12 months (median duration about 6 months) but recur less frequently. Recovery is usually complete between episodes, but a minority of patients may develop a persistent depression, mainly in old age (for which this category should still be used). Individual episodes of any severity are often precipitated by stressful life events; in many cultures, both individual episodes and persistent depression are twice as common in women as in men. The risk that a patient with recurrent depressive disorder will have an episode of mania never disappears completely, however many depressive episodes he or she has experienced. If a manic episode does occur, the diagnosis should change to bipolar affective disorder. Recurrent depressive episode may be subdivided, as below, by specifying first the type of the current episode and then (if sufficient information is available) the type that predominates in all the episodes. Includes: recurrent episodes of depressive reaction, psychogenic depression, reactive depression, seasonal affective disorder (F33. Otherwise, the diagnosis should be other recurrent mood [affective] disorder (F38. A fifth character may be used to specify the presence of the somatic syndrome in the current episode: F33. If required, delusions or hallucinations may be specified as mood-congruent or mood incongruent (see F30. This category can still be used if the patient is receiving treatment to reduce the risk of further episodes. In some instances, however, recurrent or single episodes of manic disorder, or mild or severe depressive disorder, may become superimposed on a persistent affective disorder. The persistent affective disorders are classified here rather than with the personality disorders because of evidence from family studies that they are genetically related to the mood disorders, and because they are sometimes amenable to the same treatments as mood disorders. Both early and late onset varieties of cyclothymia and dysthymia are described, and should be specified as such if required. This instability usually develops early in adult life and pursues a chronic course, although at times the mood may be normal and stable for months at a time. The mood swings are usually perceived by the individual as being unrelated to life events. Because the mood swings are relatively mild and the periods of mood elevation may be enjoyable, cyclothymia frequently fails to come to medical attention. In some cases this may be because the mood change, although present, is less prominent than cyclical changes in activity, self-confidence, sociability, or appetitive behaviour. Diagnostic guidelines the essential feature is a persistent instability of mood, involving numerous periods of mild depression and mild elation, none of which has been sufficiently severe or prolonged to fulfil the criteria for bipolar affective disorder (F31. This implies that individual episodes of mood swings do not fulfil the criteria for any of the categories described under manic episode (F30. Includes:affective personality disorder cycloid personality cyclothymic personality Differential diagnosis. This disorder is common in the relatives of patients with bipolar affective disorder (F31. It may persist throughout adult life, cease temporarily or permanently, or develop into more severe mood swings meeting the criteria for bipolar affective disorder (F31. The balance between individual phases of mild depression and intervening periods of comparative normality is very variable. Sufferers usually have periods of days or weeks when they describe themselves as well, but most of the time (often for months at a time) they feel tired and depressed; everything is an effort and nothing is enjoyed. They brood and complain, sleep badly and feel inadequate, but are usually able to cope with the basic demands of everyday life. Dysthymia therefore has much in common with the concepts of depressive neurosis and neurotic depression. If required, age of onset may be specified as early (in late teenage or the twenties) or late. Diagnostic guidelines the essential feature is a very long-standing depression of mood which is never, or only very rarely, severe enough to fulfil the criteria for recurrent depressive disorder, mild or moderate severity (F33. It usually begins early in adult life and lasts for at least several years, sometimes indefinitely. When the onset is later in life, the -107 disorder is often the aftermath of a discrete depressive episode (F32. Some types of depression previously called "neurotic" are included here, provided that they do not meet the criteria for either cyclothymia (F34. The individual depressive episodes all last less than 2 weeks (typically 2-3 days, with complete recovery) but fulfil the symptomatic criteria for mild, moderate, or severe depressive episode (F32. As noted in the general introduction to this classification, the concept of neurosis has not been retained as a major organizing principle, but care has been taken to allow the easy identification of disorders that some users still might wish to regard as neurotic in their own usage of the term (see note on neurosis in the general introduction (page 3). Mixtures of symptoms are common (coexistent depression and anxiety being by far the most frequent), particularly in the less severe varieties of these disorders often seen in primary care. Although efforts should be made to decide which is the predominant syndrome, a category is provided for those cases of mixed depression and anxiety in which it would be artificial to force a decision (F41. F40 Phobic anxiety disorders In this group of disorders, anxiety is evoked only, or predominantly, by certain well-defined situations or objects (external to the individual) which are not currently dangerous. As a result, these situations or objects are characteristically avoided or endured with dread. Phobic anxiety is indistinguishable subjectively, physiologically, and behaviourally from other types of anxiety and may vary in severity from mild unease to terror. The anxiety is not relieved by the knowledge that other people do not regard the situation in question as dangerous or threatening. Mere contemplation of entry to the phobic situation usually generates anticipatory anxiety. The adoption of the criterion that the phobic object or situation is external to the subject implies that many of the fears relating to the presence of disease (nosophobia) and disfigurement (dysmorphobia) are now classified under F45. However, if the fear of disease arises predominantly and repeatedly from possible exposure to infection or contamination, or is simply a fear of medical procedures (injections, operations, etc. Pre-existing phobic anxiety almost invariably gets worse during an intercurrent depressive episode. Some depressive episodes are accompanied by temporary phobic anxiety and a depressive mood often accompanies some phobias, particularly agoraphobia. Whether two diagnoses, phobic anxiety and depressive episode, are needed or only one is determined by whether one disorder developed clearly before the other and by whether one is clearly predominant at the time of diagnosis. If the criteria for depressive disorder were met before the phobic symptoms first appeared, the former should be given diagnostic precedence (see note in Introduction, pages 6 and 7). Most phobic disorders other than social phobias are more common in women than in men. Panic disorder as a main diagnosis should be diagnosed only in the absence of any of the phobias listed in F40. It is now taken to include fears not only of open -112 spaces but also of related aspects such as the presence of crowds and the difficulty of immediate easy escape to a safe place (usually home). The term therefore refers to an interrelated and often overlapping cluster of phobias embracing fears of leaving home: fear of entering shops, crowds, and public places, or of travelling alone in trains, buses, or planes. Although the severity of the anxiety and the extent of avoidance behaviour are variable, this is the most incapacitating of the phobic disorders and some sufferers become completely housebound; many are terrified by the thought of collapsing and being left helpless in public. The lack of an immediately available exit is one of the key features of many of these agoraphobic situations. Depressive and obsessional symptoms and social phobias may also be present but do not dominate the clinical picture. In the absence of effective treatment, agoraphobia often becomes chronic, though usually fluctuating. Diagnostic guidelines All of the following criteria should be fulfilled for a definite diagnosis: (a)the psychological or autonomic symptoms must be primarily manifestations of anxiety and not secondary to other symptoms, such as delusions or obsessional thoughts; (b)the anxiety must be restricted to (or occur mainly in) at least two of the following situations: crowds, public places, travelling away from home, and travelling alone; and (c)avoidance of the phobic situation must be, or have been, a prominent feature. It must be remembered that some agoraphobics experience little anxiety because they are consistently able to avoid their phobic situations. The presence of other symptoms such as depression, depersonalization, obsessional symptoms, and social phobias does not invalidate the diagnosis, provided that these symptoms do not dominate the clinical picture. However, if the patient was already significantly depressed when the phobic symptoms first appeared, depressive episode may be a more appropriate main diagnosis; this is more common in late-onset cases. They may present as a complaint of blushing, hand tremor, nausea, or urgency of micturition, the individual sometimes being convinced that one of these secondary manifestations of anxiety is the primary problem; symptoms may progress to panic attacks. Avoidance is often marked, and in extreme cases may result in almost complete social isolation.
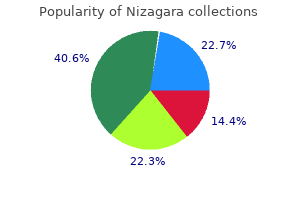
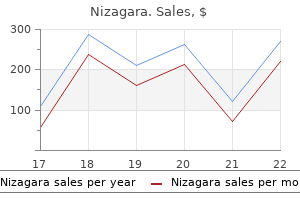
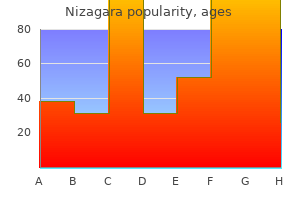
Because it is not required erectile dysfunction urinary tract infection purchase nizagara 50mg line, some providers may not routinely have it available in their practice or provide the same strength of recommendation as the required vaccines erectile dysfunction for young men buy genuine nizagara on line. First dose versus series completion First dose vaccination rates are higher than series completion rates in both males and females erectile dysfunction yeast infection cheap nizagara 100mg line. This is a challenge because it indicates children are being lost to follow-up erectile dysfunction doctors in colorado springs order nizagara with paypal, but it is also an opportunity for community pharmacies to make an impact erectile dysfunction pump implant discount nizagara 100 mg without a prescription. The assessments were created as electronic surveys erectile dysfunction age cheap nizagara 50 mg without a prescription, and the links to the surveys were sent through a variety of electronic channels. Respondents had to meet qualifying criteria for the survey including living or practicing in Michigan to ensure consistency of healthcare practice laws. Common Questions the first question asked respondents to use a sliding scale from zero through 100 percent to indicate how important they felt vaccination was in general. Many pharmacists felt vaccinations were important, but approximately 30% rated the overall importance of vaccines at 60% or less. For free response answers provided below, responses are presented as respondents typed them. Healthcare Provider Assessment Responses Do you administer any vaccines in your practicefi They stated they had some training on giving vaccination, but did not feel real confident providing. The general public is overall very ignorant of all the diseases out there partially because there are so many things to worry about. The reason I somewhat support receiving in a Pharmacy is that I have had conversations with some and they did not feel confident in providing and answering parents questions. Parent Assessment Responses 25 20 15 10 5 0 0 months through 8 9 through 10 years 11 through 12 years 13 through 17 years 18 through 26 years years Figure 6: Percent of parents responding to survey with children in different age ranges. I want them to choose whether or not to receive it, even though the recommended age is 12 years old. Currently Administers Vaccines 49% 51% Does not Currently Administer Vaccines Figure 13: Percentage of pharmacist respondents who currently administer vaccines in practice. Providers who wrote significant numbers of prescriptions filled by the pilot pharmacies and located within geographic proximity to each of the pilot pharmacies were identified. Then, the pharmacists made follow-up phone calls to the provider offices to establish a personal connection. Originally, the pharmacists were planning to visit the providers in person, but schedules and workflow made this not feasible. As a result of the outreach efforts, written contact was made with 54 provider offices. In some cases the pharmacists were not able to make contact with the provider offices after repeated phone calls. Based on the number of completed calls and the number of providers in each practice, the indirect impact was with 103 physicians, 17 physician assistants, 15 nurse practitioners, six nurses and 112 other office personnel. Reasons that practices did not want to be on the referral list included the following: not carrying the vaccine; working in a closed system that does not accept outside patients; working with a different chain pharmacy and having their patients come back directly for the second and third doses. Ten of seventeen provider offices that responded to the question said they would be willing to refer patients to the pharmacy. Reasons for not being willing to refer patients to the pharmacy include the following: they are doing just fine with having their patients complete the series; the pharmacy is too far away; they use nursing visits so patients just stop by and they prefer to administer the follow-up doses in their own office. Unfortunately, not all of the interactions with the provider offices were pleasant. Some offices were unreceptive to the calls and would not allow the pharmacist to speak to anyone beyond the receptionist. Some offices were even offended by the phone calls and felt the pharmacists should not be asking them any questions about their immunization practices. An unexpected barrier was actually being able to get past the receptionist or office manager in the physician practices to speak with other providers about partnership for this project. Since an introductory letter was sent first and then the pharmacists followed up with a phone call, the expectation was an enhanced ability to establish a relationship and partnership. Given the relatively short duration of the pilot project, it may not have been enough time to build the community connections. Perhaps the relationship development cycle for partnership is longer than anticipated and better relationships could have been established given more time. Other ideas for approaching this differently might be for the pharmacists to go to a local or state medical society meeting to introduce the concept of partnering on a larger level and then ask for partners and others to help disseminate the project to other members. Another strategy might be to have a pharmacist team up with a local industry representative who has an existing (and hopefully positive) relationship with the physician practices. Perhaps a joint effort could help start the conversation and get past that initial entry barrier. This possibility was discussed but was not executed during the pilot project due to time constraints. Pharmacists and pharmacy technicians involved in the pilot program received significant education since they would be providing direct patient care. A flyer was mailed to 2,550 pharmacist members notifying them about the new website resources. Age-appropriate, patient-friendly handouts printed along with the screening tools with each prescription meeting the defined criteria. These education handouts went home with 2,342 patients and parents, along with their other prescription paperwork, for their reference at home. The best patient education occurred through conversations between the patients and pharmacists. At least 429 pharmacist-patient conversations occurred based on the 429 completed screening tools. Provider education was conducted as part of the provider outreach strategy discussed above. Current staffs at the local health departments already have a difficult time meeting the inspection requirements due to time and financial constraints. The state is still conducting the pilot program and will not make decisions regarding further expansion of the program for pharmacy involvement until the pilot is complete at some undetermined point in the future. If patients have straight Medicaid, the pharmacy does receive a small dispensing/administration fee. To be able to get the pilot pharmacies up and running in time to get several months of data, we started the pharmacist training and workflow tool development process first. It would have been better to complete the stakeholder assessments first and the provider outreach visits or calls. The training program we created for the pharmacists and pharmacy technicians was very successful. Most felt they needed the additional focused education to reach that level of confidence in making a strong recommendation. We used a screening tool to target potential patients, but those become less effective as time progresses. We would select pharmacies near college campuses while classes were in session to target the 18 through 26 year old patients. Another piece of information that was discovered during one of the pharmacist interviews is that we might be missing a large part of the population that is just not accessing healthcare at all. If the target audience is adolescents >15 years old, how would you structure the programfi If the target of the program was only adolescents 15 years and older, we could have changed the screening tool to be more selective to that age group. We also would consider outreach through high schools and colleges to target the older demographic which still needs all three doses of the vaccine. This eliminates a huge barrier for many commercially insured patients in Michigan. Having additional payers on board to work on this project would have been helpful. We made repeated attempts to engage with payers and find someone to talk to about the project but no one was willing to engage in such a discussion. Most cited the need for better protection against cancer among the residents of their communities. Having a pharmacist or pharmacy technician walk them through the questions greatly improves the success rate. If available, accessing a state immunization registry before a potentially eligible patient visits the pharmacy to pick up a prescription can prepare the pharmacist with a list of recommended vaccines customized for that patient. Face-to-face interactions with the local physician groups, perhaps by partnering with industry representatives or by visiting medical association meetings, may help overcome the initial contact barriers encountered from receptionists and office managers. Patients and parents hear enough confusing messages from other sources; they need to be able to trust the consistency and strength of the recommendation from their pharmacist, a trusted healthcare provider. Some additional steps or changes may be needed to for the technology to work for follow-up dose reminders, but it can be a great tool for helping patients complete their series. For small chain pharmacies, working with a committed team in one pharmacy to optimize the workflow processes before spreading it to more locations may be a good way to start. Fainting is a more common side effect from vaccination in adolescents than in adults. With increased vaccine administration to younger patients, the possibility of a patient fainting in the pharmacy setting also increases. Pharmacies can easily plan for this and have proper procedures in place in the event that it occurs. Members were notified of the new content through a flyer included in their annual membership renewal notice. The learning objectives and posttest questions were slightly different for each audience. Fever (correct answer) Explanation: Fever was rarely reported in the clinical trials as compared to the injection-site reactions and headaches which were reported at rates >10%. Participants in the hybrid training watched a video recording of the presentation. List the steps for integrating the vaccination screening tool into the pharmacy workflow. False Explanation: this is one of the strategies being employed as part of the grant project. Informational handouts from reputable sources are helpful to provide additional information. Internet research and experiences of friends can provide unreliable, unscientific information. Identify strategies for technicians to use when talking with patients about the vaccination screening tool and pharmacist recommendations. False (correct answer) Explanation: the largest predictor of vaccination is the strength of the recommendation given by their healthcare provider. Patients and parents rely on trusting relationships with healthcare providers when making decisions. When making decisions of high concern (for example, decisions to vaccinate), they rely more heavily on which component of trustfi At what point in the prescription process will the immunization screening tool/survey print for appropriate patientsfi Point-of-sale checkout Explanation: the screening tool/survey will print during final verification by the pharmacist and will be placed in the bag with the prescription and other information so it is ready and available for the patient/parent when they pick up the prescription. What is an important opportunity the technician will often have to increase utilization of the screening tool/surveyfi Asking the patient/parent to complete the printed screening tool/survey which finalizing prescription checkout b. Alerting the pharmacist when a patient/parent completes the screening tool/survey so the pharmacist is able to counsel d. All of the above (correct answer) Explanation: the technician is often the point of the contact for the patient/parent and can take advantage of all of the opportunities listed to increase participation. What kind of impact do you think you had on your patients and community as part of this projectfi Do you feel like you had adequate staffing to fully participate in the pilot projectfi Advisory Committee Materials Advisory Committee Participant Email Invitation Greetings! The purpose of the Committee is to provide input and suggestions that will help us obtain valuable information through this grant project. If you are personally unable to attend the meeting but know someone who would be interested in participating on our Advisory Committee, please respond to this email with his or her contact information so I may contact them personally. Prefimeeting materials will provide additional details about the grant, expectations of Committee members and the desired outcomes from the live meeting. Our diverse group of stakeholders includes physicians, pharmacists, industry representatives, public health officials and parents. We appreciate your patience and understanding while facility preparation is completed.
Nizagara 100 mg without a prescription. Types Of Herbs For Impotence | Erectile Dysfunction Natural Herbal Remedies.
References
- Walkey AJ, O'Donnell MR, Weiner RS. Linezolid vs. glycopeptide antibiotics for the treatment of suspected methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus nosocomial pneumonia. Chest. 2011;139:1148-1155.
- Dole WP, Nuno DW: Myocardial oxygen tension determines the degree and pressure range of coronary autoregulation, Circ Res 59:202, 1986.
- Kotchen TA. The search for strategies to control hypertension. Circulation 2010;122: 1141-1143.
- Holman WL, Park SJ, Long JW, et al. Infection in permanent circulatory support: experience from the REMATCH trial. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2004;23:1359-1365.