John R. Wingard, M.D.
- Professor
- Department of Medicine
- University of Florida
- Director of Bone Marrow Transplant Program
- Department of Medicine
- University of Florida Shands Cancer Center
- Gainesville, Florida
When he later changed affliations allergy testing supplies order rhinocort 200 mcg fast delivery, Ken Hartigan-Go assumed leadership and broadened the scope of the topic group allergy treatment in toddlers rhinocort 100mcg on line. Subsequently allergy treatment bioallers best purchase for rhinocort, Hartigan-Go passed leadership to Priya Bahri who stepped in to lead the topic group in late 2015 and forged a new direction based on member and broader stakeholder input allergy testing york region buy rhinocort 200 mcg. In some cases organizations changed names over the course of this project or contributors changed affliations; this is not always refected in the listing allergy treatment 3rd rhinocort 200mcg otc. The list generally includes the affliation of the contributor during the time he or she participated in the topic group allergy treatment results discount rhinocort 200 mcg with mastercard. Abdoellah, Indonesia National Agency of Drug and Food Control (Regulatory Siti Asfjah authority) 2. Hartigan-Go, Ken Philippines Dept of Health (Public health authority), Asian Institute of Management 11. Their comments were welcoming and supportive to the report, and clarifcations on the recommendations and updates to some of the references, as well as additions to the reading list have been implemented in the fnal report in response to the comments. Julia Tainijoki-Seyer World Medical Association (during public consultation commented for the organization) 8. Robert Pless Health Canada (during public consultation commented in private capacity) 9. Sourcing from existing guidance documents and compiling recommendations relevant from a regulatory perspective, the Guide provides a common ground in a way that has not been achieved otherwise at global level. The Guide stresses the fundamental importance of regulatory bodies having a system in place with skilled persons who can effciently run vaccine safety communication in collaboration with stakeholders. This publication seeks to describe the best treatments and practices based on the scientifc evidence available at the time of writing as evaluated by the authors and may change as a result of new research. Readers need to apply this knowledge to patients in accordance with the guidelines and laws of their country of practice. Some medications may not be available in some countries and readers should consult the specifc drug information since not all dosages and unwanted efects are mentioned. Organizations, publications and websites are cited or linked to illustrate issues or as a source of further information. This is an open-access publication under the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial License. Use, distribution and reproduction in any medium are allowed without prior permission provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. Geneva: International Association for Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Allied Professions 2014. The notion of sleep as a state characterized by a suspension of declared voluntary functions continued to be predominant until the 19th century. As such, sleep is considered an active Confict of interest: none rather than a passive process. Despite remarkable progress in the feld of sleep declared medicine in the past century, the answer to the question: why do we sleep However, a large amount of empirical evidence shows that alterations in sleep quantity or quality do impact on cognitive, afective and, more generally, psychological functions. The present chapter is intended as a practical guide to help clinicians recognize, diagnose and manage the more common sleep disturbances in children and adolescents according to available empirical evidence or clinical experience rather than as an overview of the science of pediatric sleep medicine. Nonetheless, before discussing the presentation and management of the most relevant sleep disorders in children, we will provide an introduction to the basic principles of sleep and sleep medicine to better understand disorders of sleep. Finally, given the international readership to which this chapter is addressed, we will discuss some issues pertaining to pediatric sleep medicine in low and middle-income countries. The former include posture, mobility, response to stimulation, level of alertness, eyelids, and eye movement (Table I. In general, sleep requirements decrease from the newborn (about 16 h/day of sleep) to the young child (3-5 years old: 11 h/day), to the older child (10-11 years old: 10 h/day), to the adult (7. Sleep cycles last about 45 minutes in young children, 60 minutes in 9-year-olds, and 90-110 minutes after the age of 10 (as in adults). Spindles and K complex are fully formed by the age of 3 and 6 months, respectively. Recommendations for healthy sleep usually include guidance across a wide range of activities such as adoption of a bedtime routine, consistent bedtime and wake time, a quiet, dark and cool bedroom, avoidance of cafeinated products, and daily physical activities. Healthy sleep practices are also a fundamental component of sleep education designed to prevent sleep problems from developing (primary prevention), to address poor sleep quality (secondary prevention), and to treat existing sleep disorders. Education about sleep hygiene is a standard component of treatment for typically developing children with sleep problems as well as for those with chronic medical conditions and psychiatric disorders. Homeostatic sleep/ wake regulation refers to the capability of the brain to compensate for transient sleep loss by increases in sleep duration and sleep intensity. The two-process model of sleep/wake regulation assumes two independent but interacting processes, a circadian process (process C) and a homeostatic process (process S) that *en. Process C determines the circadian Healthy sleep practices are potential mediating factors between variation of a wake signal biological sleep needs and environmental circumstances which facilitate or impede independent from prior wake time. For example, one of the most important elements of a healthy sleep practice be considered as drive for is a regular sleep and wake schedule. A consistent bedtime and wake time helps sleep that is proportional to prior wake time. Process to reinforce circadian rhythms and optimize the sleep drive, processes which are S is low in the morning instrumental in regulating healthy sleep-wake cycles. Subjective assessment relies either on unstructured questions that explore the most relevant sleep-related behaviors (see Table I. Parents, and children if appropriate, are asked to write details about what time the child goes to bed, how long does it take to fall asleep, the frequency and duration of nighttime awakenings, the timing and duration of daily naps, the time of waking up in the morning, and the total duration of sleep. Diffculty with falling asleep (within 20 minutes after going to bed, according to some authors). Factors that may contribute to sleep onset diffculties include psychiatric Sleep onset diffculties conditions. Night wakings that require parental intervention for the child to return to sleep are often related to inappropriate sleep onset associations (conditions the child learns to need in Night awakenings order to fall back to sleep). Sleep duration is variously Sleep duration defned as the time asleep at night, or as time asleep plus time in bed awake at night, or as the total time asleep across 24 h. Behaviors such as the child refusing to wake up by himself or diffculties getting out of bed Diffculties with in the morning. They may be the consequence of inadequate sleep or the result of parental morning awakenings diffculties in setting limits and managing behavior. It is characterized by persistent tiredness and lack of energy with a tendency to fall asleep during the day. Restless sleep Sleep characterized by excessive movements of some parts of the body or the whole body. Parasomnias are undesirable physical events or experiences that occur during entry into sleep, within sleep, or during arousal from sleep. Most mental health professionals would not use these tools in their practice but should be aware of them and of when to refer their patients to a specialist for objective sleep assessment. Rather, they lump children and adults together, although in some instances developmental features of particular sleep disorders are specifed. Actigraphy Sleep parameters (sleep/wake periods, total duration of sleep, number of arousals, and length of sleep onset) are inferred by the patterns of rest/movement. It consists of four or fve 20-30 minute opportunities to have a nap given at 2-hour Multiple sleep latency intervals during the day. The lower it is, the higher the sleepiness multiple sleep latency test during daytime the number of apnea and hypopnea episodes per hour (apnea is defned as a cessation of airfow for at least 10 seconds; hypopnea is defned as a Apnea-hypopnea index 50% reduction in airfow [measured with a valid technique] or a reduction in airfow associated with a 3% fall in arterial oxygen saturation or an arousal) Child sleeping with an ambulatory cardiorespiratory monitoring Sleep disorders I. Since it is impractical to present the diagnostic work up and the management of each disorder, we will focus on the most common and relevant in clinical practice with children and adolescents. Prevalence of pediatric insomnia is estimated at about 1% to 6% in general pediatric populations, with a much higher prevalence in children with neurodevelopmental and chronic medical and psychiatric conditions (Owens & Mindell, 2011). When bedtime resistance and disruptive nighttime awakenings are included, the prevalence of sleep-disrupted behavior approaches 25% to 50% in preschool children (Owens & Mindell, 2011). It has been proposed that persistent insomnia may also represent an early sign of emotional distress in susceptible children with poor sleep homeostasis (Ivanenko et al, 2004). The child is usually unable to fall asleep in the absence of these conditions at both bedtime and on waking up during the night. Controlled comforting is a behavioural strategy for dealing with persistent settling and waking problems in young children. The aim is to help children learn how to settle themselves to sleep, rather than parents feeding, patting or cuddling them to sleep. It involves brief checks and reassurance of babies while they are learning to settle. A 5-year follow up study of children with sleep problems at 7 months found that behavioral sleep techniques had no long-lasting effects (positive or negative) on them by age 6. The authors concluded that parents and health professionals can confdently use these techniques to reduce the short to medium-term burden of infant sleep problems and maternal depression (Price et al, 2012). Set your own intervals of time based on how check on your baby when the set time is up. Graduate extinction techniques and controlled crying are more appropriate for younger children, whereas cognitive and coping strategies are better suited to school-aged children. The infant learns to self-soothe when realizing that nighttime crying does not result in parental attention Extinction with parent the parent remains in the room during extinction, acting as a reassurance for the presence child but providing little interaction this involves ignoring negative behaviors. The parent gradually increases the amount of time Graduate extinction between crying and parental response. The Bedtime fading goal is for the child to develop a positive association between being in bed and falling asleep rapidly.
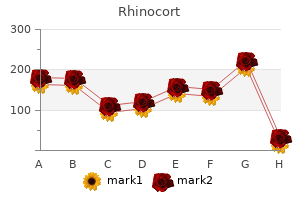
Delta that is polymorphic (or arrhythmic) is composed of slow-wave activity that is 3 allergy steroid shot cheap generic rhinocort canada. Polymorphic delta activity when localized is indicative of an underlying supratentorial lesion affecting the white matter of the ipsilateral hemisphere allergy forecast waukesha wi order genuine rhinocort line. The greater the state-independ ence and persistence allergy forecast utah buy 200mcg rhinocort otc, the greater the degree of correlation with a struc tural lesion allergy symptoms nasal drip generic rhinocort 100mcg. Localized polymorphic delta allergy symptoms zyrtec cheap rhinocort 100 mcg without a prescription, however allergy symptoms yellow mucus buy rhinocort 100 mcg amex, may be seen as a transitory phenomenon from head injury, transient ischemic attack, migraine, and during a postictal state. Asymmetry of sleep spindles in a 36-year-old patient with a right thalamic glioma. Sleep elements are normally maximal in frequency in the central location, although they may appear in the frontal regions as well. A frequency of 12 to 14 Hz is observed in the central regions and is the distinguishing charac teristic of stage 2 sleep. Spindles are very stable in the bilateral appear ance, and a persistent slowing of frequency or unilateral appearance should be regarded as an abnormal nonepileptiform feature. The electroencephalogram in diffuse encephalopathies: electroenephalographic correlates of grey and white mat ter lesions. For example, central, parietal, and occipital spikes, in gen eral, are more benign regions than frontal and temporal locations and have a relatively reduced potential for epileptogenicity in the absence of a structural lesion. They may help provide information useful in localizing the epileptogenic zone for the purposes of surgical treat ment. Furthermore, there is treatment information that can be clinically relevant following therapy. The location of focal interictal epileptiform discharges vary with respect to the potential to generate clin ical seizures and also the behavioral manifestations that are likely to occur. Intracranial versus scalp recording (in the bottom six channels) during a presurgical evaluation of intractable epilepsy. Therefore, difficulty with source detec tion at the level of the scalp may arise because of deep-seated foci. Note a single sharp wave in the first second and a spike-and slow wave complex in the last second. Both spikes and sharp waves are referred to as interictal epileptiform discharges (transients). Both spikes and sharp waves are generated at the top of the cortical gyrus and have a polar ity that is most often negative at the surface of the scalp recording. The location usually determines the potential for epileptogenicity with temporal locations usually carrying the highest association with clinical seizure expression. Left temporal sharp waves in a 43-year-old man after left tem poral lobectomy evaluated for reoperation. Interictal epilep Ptiform discharges (spikes and sharp waves) are almost always sur face negative, generating the typical negative phase reversal. The situation encountered most commonly in clinical practice in which they may have a positive polarity is in patients who have had surgery and altered cortical anatomy. Anterior temporal spikes or sharp waves often have a clinical association with complex partial seizures of temporal lobe origin more than 90% of the time. Focal slowing and the presence of bilateral discharges appear more likely to be equally represented. Notice the central field of spread of the spikes and low-amplitude right frontal positivity. This dipole characteristically reveals a maximum negativity in the cen trotemporal region and a contralateral maximum positivity in the frontal (or vertex) region that is best demonstrated on referential montages. Transverse montages are best to distinguish a lateralized generator from two discrete bisynchronous generators. Some conditions may give rise to central spikes without epilepsy and include cerebral palsy, migraine, and inherited trait without seizures. Isolated mid line spikes, polyspikes, or pathological sharp waves are most often noted at the central vertex, and have a high association with epilepsy. A single right occipital spike-and-slow wave discharge shown in both a bipolar and reference montage (last two channels). Multifocal independent spike discharges seen in a patient with encephalopathic generalized epilepsy. Mental retardation and cerebral palsy are common underlying substrates for patients with multifocal independent spike discharges. There may be a primary site of focal dysfunction or be associated with concomitant generalized epileptiform discharges such as with the Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Generalized epileptiform discharges vary in duration and may be seen with or with out clinical signs or even appear less often as an inherited trait without seizures. Self-limited photoparoxysmal response in a patient without seizures evaluated for headaches. It appears as a bilat eral, synchronous, symmetrical, surface-negative spike maximal in the frontal-central regions, followed by a surface-negative slow wave in a longitudinal bipolar montage. Response times may be impaired regardless of burst dura tion, although longer bursts imply longer periods of impaired respon siveness. The discharges are maximal in the frontal regions with two or more high-voltage surface-negative spikes best described as polyspikes (or multispikes). Note the high-ampli tude, chaotic background and multifocal spikes within the left hemisphere. A high-voltage background composed of disorgan ized slow theta and delta frequencies is seen in addition to nearly con tinuous multi-focal interictal epileptiform discharges. Modified patterns are noted with variations in amplitude and hemispheric pre dominance and may occur with attenuations that may correlate with infantile spasms. This most often consists of a biphasic or triphasic surface negative sharp wave followed by a slow wave in a bilateral, synchronous, symmetri cal, frontocentral complex. It is pri marily seen during sleep and consists of diffuse, bilateral bursts of 15 to 20 Hz frontally predominant bursts of fast frequencies. Variable frequencies, voltages, and durations may occur, although they usually last several seconds. This feature frequently has no overtly detectable clinical manifestations, although it may correlate with tonic seizures when occurring while awake or with durations of >6 sec. Patterns of cortical discharges and their rela tion to routine scalp electroencephalography. Electroencephalogram epileptiform abnor malities in candidates for aircrew training. Additionally, classification of the seizure T type for the purposes of identifying the type of epilepsy to direct treatment can be deduced. These ictal patterns may serve as the basis for localization of recurrent seizures in epilepsy that are useful not only in the diagnosis but also in the treatment selection and prognosis. Ictal dis charges are most frequently composed of repetitive rhythmic frequencies as opposed to simple repetition of interictal epileptiform discharges. In idiopathic generalized epilepsy, several seizure types may overlap and appear as epilepsy syndromes. Generalized seizures associated with symptomatic generalized epilepsy are more heterogeneous but are characteristic of patients with diffuse structural injury. However, even a single spike-and-wave discharge may be associated with a subtle behavioral alteration of responsiveness that is not clinically discernible with gross testing modalities. Notice the change in alerting seen after the 1-sec burst of generalized spike and polyspike-and-waves in the above figure. These discharges may start at a rate of >3 Hz, but eventually slow down to a discharge frequency slightly above 2 Hz. Maximum amplitude is in the fronto-central region, often with phase reversals bilaterally at F3 and F4. In some patients, the spike component may be subtle or absent, and replaced by rhythmic slow activity. The polyspike for mation is evident in the example above and is associated with myoclonus at the onset of this seizure. Isolated polyspike-and-wave discharges may be associated with myoclonus that is obscured by an overriding artifact. Infantile spasm noted in second 7 above with an electrodecre mental response obtained in a 3-year-old child with tuberous sclerosis. There are several forms that may occur depending upon the degree of somatic involvement, and are typ ically associated with mental impairment. Low-voltage fast frequencies associated with a generalized attenuation of the background may also be evident during a tonic seizure. Right temporal 6 to 7-Hz rhythmic ictal theta discharge at seizure onset in a patient with temporal lobe epilepsy. A frequent ictal pat tern of mesial temporal origin is the sudden appearance of localized or regional background attenuation, build-up of 4 to 7-Hz rhythmic activity, increasing in amplitude as it slows to 1 to 2 Hz. Left temporal neocortical seizure onset with rhythmic 3-Hz delta maximal in the mid-temporal derivation prior to rapid generalization. Although it may be difficult to clinically distinguish neocortical temporal lobe seizures from mesial temporal lobe seizures, they may have a widespread hemispheric onset, begin in the mid-temporal derivations at <5 Hz, have rapid propagation to extratemporal structures, and have a greater likelihood to secondarily generalize as seen above. In the above exam ple, a right anterior temporal lobe lesion was seen and created the appearance of a right frontal discharge initially present as a burst of repetitive spikes that evolved to an irregular right fronto-temporal theta rhythm. Lateralization and regionalization of the ictal activity are then complementary to the remaining parameters of the presurgical evaluation to demonstrate concordance for the purposes of epilepsy surgery. Interictal epileptiform discharges are notably absent in 30% of patients with frontal lobe epilepsy. Orbitofrontal and mesial frontal may not manifest interictal or even ictal discharges at all. Diffuse electrodecremental response in a patient with a sup plementary motor seizure. The tracing shows high-frequency, mu-like arcuate wave forms focally over the left parietal C3-P3 derivations at 10 Hz in the region of a brain tumor. Somatosensory Pinvolvement may yield a perception of tingling, formication, pain, heat, movement, or dysmorphopsia, typically of the distal limb or face. As in frontal lobe epilepsy, only a small number of those with parietal ictal onset are focal. Spread may occur to the supplementary motor area or temporal area and result in electrographic lateralization or even localization late in the seizure onset. The patient above noted paroxysmal right arm and leg tingling during the recording. There may be illusions that objects appear larger (macrop sia), smaller (micropsia), distorted (metamorphopsia), or persistent after the visual stimulus (pallinopsia). High-frequency discharges at the temporoparieto-occipital junction can induce contraversive nys tagmus and eye and head deviation. Seizures may occur without awareness or be very subtle such that clinical signs are not noted. When testing is performed, some seizures exhibit no evidence of interruption in behavior. In the patient above with encephalopathic generalized epilepsy, the seizures were unassociated with any clinical signs despite behavioral testing (counting). Note the evolution of the rhythmic myogenic artifact that occurred with repetitive jaw movement mimicking an epileptic seizure. While the precise inci dence is undefined, they account for 20% to 25% of admissions to hospital based epilepsy monitoring units and are about as prevalent as multiple sclerosis. Nonepileptic encephalopathic recordings as well as those that are epileptiform occur in addition to those that include both forms with dynamic transition. In stupor and coma, slower waveforms are seen that are morphologically different than those that are seen during sleep. However, some patterns have special prognostic significance and will be represented in the following section. Intermediate examples may occur, with the evolution of a focal to a generalized pattern, or the reverse. Between individual discharges, there may be preservation (or conversely ablation) of background activity. These may wax and wane and occur in a frequency of less than every several seconds to >3/sec. They may contain spike, sharp wave, poly spike morphologies, or mixtures of these features. The etiology for periodic patterns is nonspecific, although, when iden tified bilaterally, they usually reflect an acute or subacute, diffuse, encephalopathic process. When identified unilaterally, they often reflect a focal structural manifesta tion when lateralized and persistent. Morphology, field of involvement, and reactivity are important in quantifying the patterns within the context of the state of consciousness.
Consider increasing fluid requirements in patients who develop fever allergy testing queenstown purchase generic rhinocort on line, nausea allergy count chicago order rhinocort online from canada, vomiting mould allergy treatment uk buy rhinocort 200 mcg without a prescription, or diarrhea; the initiation of medication allergy shots oral cheap 100 mcg rhinocort with amex, physical activity allergy testing labcorp buy cheap rhinocort 200 mcg on-line, and inclement hot or dry weather may also necessitate increased fluid intake (9) allergy symptoms ears popping buy rhinocort 100mcg on-line. Fluid restrictions may be indicated for patients with renal or hepatic failure (9). However, it is difficult to adequately study these nutrients effectively due to the inability to separate the effects of individual nutrient deficiencies from the effects of generalized malnutrition on the immune system (1, 21, 42). Routine biochemical assessment of vitamin and mineral levels is recommended to determine the best treatment options if symptoms are present and deficiencies are suspected (1, 9). Supplementation based on levels described in the Dietary Reference Intakes that remain below the upper limits of safety seems prudent in the absence of sufficient evidence (9). Bone density can be preserved through the maintenance of optimal weight and the prevention of rapid weight loss (1). Vitamin K, vitamin C, and zinc are also important for bone formation and should be included in an adequate diet (1, 43). Use of herbal supplementation: Supplemental nutrients, herbs, and other medications may be processed by the pathways used by antiretroviral medications. As a result, the levels of the supplements or medications may be greater or less than the expected levels (1). Potential interactions include the reduction of drug efficacy during the concomitant use of St. Early nutrition intervention is very important, and routine nutrition assessment should include monitoring of height, weight, and head circumference with comparison to growth standards for age and sex (1). Additional serial measures for anthropometry may include thigh circumference and mid-upper arm circumference (1). The registered dietitian must consider the adverse influences of various medications on indicators of nutrition status and metabolic indicators of disease risk (1). The clinician must recognize that nutrients and nutritional status can affect medication absorption, utilization, elimination, and tolerance (1, 48). Patient adherence to the prescribed medication regimen is affected by negative side effects, changes in body composition (eg, body fat changes as seen in lipodystrophy), and body image issues (1). Emerging drugs under investigation include a class of maturation inhibitors and other medications that boost the levels of antiretroviral medications (1). When using ritonavir and nelfinavir, men experience more diarrhea, while women experience nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain more frequently than men (1). It is important for the clinician to consider these differences when assessing nutritional status and medication therapies. Medications may be used to control symptoms and conditions including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, mouth and throat sores, and organ diseases (1). Two commonly used medications, megestrol acetate (Megace) and dronabinol (Marinol), are currently approved for appetite stimulation. Coadministration of testosterone with megestrol acetate has not been shown to increase lean tissue accrual. However, anabolic steroids can cause liver toxicity and negative changes in lipid profiles (1). The use of testosterone and recombinant human growth hormone to treat wasting and central fat accumulation has been explored (50). Nutrition Intervention and Monitoring Symptom management is an important component of nutrition intervention and monitoring (1). Complications are diverse and develop frequently, interfering with nutritional intake and outcomes. Fever Recommend small, frequent, nutrient-dense Nausea foods; eating in a pleasant atmosphere; Vomiting and easy-to-prepare food or assistance Diarrhea with meals. Anxiety Consider vitamin and mineral supplements if Depression symptoms or biochemical tests indicate Other medical therapies deficiency. Fever Recommend small, frequent feedings; dry Medical therapies foods, soft foods, cold or room temperature foods, and salty foods; elevation of upper body during and after meals; and liquids between meals. Consider vitamin and mineral supplements if symptoms or biochemical tests indicate deficiency. Antibiotic therapy Recommend oral rehydration; replace Infection electrolytes; increase soluble-fiber foods; Foodborne or waterborne illness evaluate tolerance to gas-forming foods, Food intolerance fat, and lactose. Medical therapy Consider yogurt or probiotics if long-term Anxiety antibiotic therapy is required. Stress Consider vitamin and mineral supplements if symptoms or biochemical tests indicate deficiency. Infection Recommend soft, nonspicy, nonacidic foods; Malnutrition pureed foods or thickened liquids; and oral Oral and esophageal candidiasis supplements. Kaposi sarcoma and other Consider a topical analgesic to decrease malignancies mouth pain. Infection Recommend, small, frequent feedings; Nausea nutrient-dense foods; liquids between meals; and avoidance of greasy, fried foods and gas-forming foods. Infection Recommend alternative foods and textures; Gastrointestinal disturbance evaluate patient for nutrient deficiencies. Poor dentition Consider medical nutritional supplements as Genetic cause tolerated. Recommend small, frequent feedings; experiment with a wide variety of foods and seasonings and alternative protein sources. Nutrition prescription: the registered dietitian should determine the appropriate mode of nutrition support based on the nutrition assessment and diagnosis. Meal planning using guidelines established for lipid management and diabetes management may also be necessary in patients who develop lipodystrophy or glucose intolerance related to medication management (1, 9). Consider the following information when determining the nutrition prescription: Oral feedings are preferred over any other feeding method. Nutrient-dense foods and supplements should be used to support maintenance and restoration of nutritional status and body weight. Foodborne illnesses often cause symptoms similar to those of influenza (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, fever, and cramping). In addition, two studies showed that when education was part of a home-delivered meal program, there was strong adherence to food safety guidelines (Grade I) (1, 21). Patients should be provided with information that fits their individual lifestyles in terms of shopping, cooking, storing food, and dining out (9). If food will be in the car for longer than 30 minutes, use a cooler to keep it cold. Foods left at room temperature for longer than 2 hours are susceptible to bacterial growth. Shallow containers will help the leftovers cool more quickly to the proper temperature. Place the frozen foods in a plastic bag or on a plate to prevent juices from dripping onto other foods. Preparing Food Wash hands with antibacterial soap and warm water before and after handling food, and especially after handling raw meat, poultry, and fish. Always wash contact surfaces and utensils with a dilute bleach solution immediately after preparing these products. These foods contain raw seafood, meat, poultry, or eggs and therefore may contain harmful pathogens (bacteria). Meeting these temperature requirements does not necessarily mean that the food is well done. An instant-read thermometer is different from a meat thermometer in that it does not stay in the meat while cooking. This is especially important in a restaurant where you may not be able to check the internal temperature. Eggs that are cooked over easy or undercooked increase the risk of salmonella infection. Bones can shield the surrounding meat from the microwaves and therefore leave some meat undercooked. Water Safety Bacteria that may contaminate a water supply include Giardia, Cryptosporidium, Microsporidia, and Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare. Check to see that burgers are no longer pink in the middle and the juices run clear. Often fruits and vegetables are not washed thoroughly, and prepared foods are not kept at proper temperatures to prevent bacteria from thriving. If not, it may mean that the wait staff and cooks cannot wash their hands properly after using the restroom. Beverages made with boiled water, such as coffee or tea, are safer to drink, as are canned or bottled carbonated beverages, beer, and wine. Be aware that not all countries have the same high standards for sanitation and food safety. Position of the American Dietetic Association: nutrition intervention in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Schindler K, Rieger A, Tura A, Gmeinhardt B, Touzeau-Romer V, Haider D, Pacini G, Ludvik B. Interpreting indicators of iron status during an acute phase response-lessons from malaria and human immunodeficiency virus. Shah M, Tierney K, Adams-Huet B, Boonyavarakul A, Jacob K, Quittner C, Dinges W, Peterson D, Garg A. More than half of people aged 60 to 69 years and approximately three fourths of people aged 70 years and older have hypertension (1). Based on data from the Framingham Heart Study, people who are normotensive at 55 years of age have a 90% lifetime risk of developing hypertension (3). For every 20 mm Hg systolic or 10 mm Hg diastolic increase in blood pressure, the mortality from ischemic heart disease and stroke doubles. Data from the Framingham Heart Study indicate that blood pressure values in the range of 130 to 139 mm Hg systolic and 85 to 89 mm Hg diastolic are associated with a more than 2-fold increase in the relative risk of cardiovascular disease when compared with blood pressure levels below 120/80 mm Hg (4, 5). Lifestyle modifications are recommended to reduce the risk for developing hypertension. For patients who have diabetes mellitus or kidney disease, drug therapy should be considered if a trial of lifestyle modifications fails to reduce blood pressure to 130/80 mm Hg or less. Prehypertension is not a disease category, rather it is a designation that identifies individuals at high risk of developing hypertension (2). Individuals in the prehypertension category are advised to adopt lifestyle modifications, including dietary modifications and physical activity, to reduce their risk of developing hypertension. For patients who have prehypertension and diabetes mellitus or kidney disease, drug therapy should be considered if lifestyle modifications fail to reduce blood pressure to 130/80 mm Hg (2). The treatment goal for individuals who have hypertension and no other medical conditions is a blood pressure of 140/90 mm Hg or less (2). For individuals who have hypertension and diabetes mellitus or kidney disease, the treatment goal is 130/80 mm Hg (2). The increase in systolic blood pressure continues throughout life, in contrast to diastolic blood pressure, which increases until 50 years of age and then tends to level-off during the next decade. Systolic hypertension is the most common form of hypertension in people older than 50 years. The diastolic blood pressure is a more potent cardiovascular risk factor than systolic blood pressure prior to 50 years of age; thereafter, systolic blood pressure is more important (2). Recent data indicate that 64% of American adults are either overweight or obese (9). The consumption of processed foods accounts for 75% of the daily sodium intake (2). Fewer than 20% of Americans engage in physical activity (10), and fewer than 25% consume five or more servings of fruits and vegetables daily (11). The patient should be advised not to use herbal supplements, such as ephedra (ma huang) and bitter orange, that increase blood pressure (2). Patients who take monoamine oxidase inhibitors should be advised that consumption of licorice and tyramine-containing foods will increase their blood pressure (2). Accurate Blood Pressure Measurement the ausculatory method of blood pressure measurement with a properly calibrated and validated instrument is recommended (6, 7). The patient should be seated quietly for at least 5 minutes in a chair (rather than on an exam table), with feet on the floor and an arm supported at heart level. Caffeine, exercise, and smoking should be avoided for at least 30 minutes prior to blood pressure measurement (2). An appropriate-sized cuff (cuff bladder encircling at least 80% of the arm) should be used to ensure accuracy. The systolic blood pressure is the point at which the first two or more sounds are heard (phase 1), and the diastolic blood pressure is the point before the disappearance of sounds (phase 5) (6). Hypertension in Children and Adolescents In children and adolescents, hypertension is defined as elevated blood pressure that persists on repeated measurement at the 95th percentile or greater for age, height, and sex (2).
The rectum stores stool prior people think they are constipated if they do to a bowel movement allergy testing cpt cheap rhinocort 200mcg with visa. Bowel movement allergy testing kalamazoo purchase rhinocort without a prescription, stool moves from the rectum to movements may occur three times a day or the anus allergy symptoms coughing itchy throat buy 100mcg rhinocort free shipping, the opening through which stool three times a week allergy count safe 200 mcg rhinocort, depending on the person allergy testing without insurance buy rhinocort pills in toronto. Constipation can be acute allergy shots effectiveness purchase rhinocort 200mcg amex, which means sudden and lasting a short time, or chronic, which means lasting a long time, even years. Understanding the causes, prevention, and treatment of constipation can help many people take steps to fnd relief. People of any age, race, or the most common cause of constipation is a gender can get constipated. Fiber is a substance constipation most often are women, adults in foods that comes from plants. Fiber helps ages 65 and older, non-Caucasians, and stool stay soft so it moves smoothly through people in lower socioeconomic classes. Liquids such as water and juice Constipation is also a common problem help fber to be more effective. They may lose interest in relieve pain from things such as a broken eating because food does not taste the same bone, tooth extraction, or back pain. The colon absorbs too much water from the stool, making Lack of Physical Activity it hard and dry. Hard, dry stool is more A lack of physical activity can lead to diffcult for the muscles of the rectum to constipation, although scientists do not know push out of the body. For example, constipation often occurs after an accident or during an illness when a Common factors or disorders that lead to person must stay in bed and cannot exercise. Neurological disorders, such as spinal cord Constipation can also be caused by overuse injury and parkinsonism, affect the brain and of over-the-counter laxatives. Parkinsonism is any condition that medication that loosens stool and increases leads to the types of movement changes seen bowel movements. Metabolic disorders, feel relief when they use laxatives, they such as diabetes and hypothyroidism, disrupt usually must increase the dose over time the process the body uses to get energy from because the body grows reliant on laxatives food. People can also become push outward through weak spots in constipated while traveling, because their the colon wall; the pouches are called normal diet and daily routine are disrupted. Functional constipation often results from problems How is the cause of with muscle activity in the colon or anus that delay stool movement. Functional constipation is diagnosed in To diagnose the cause of constipation, the people who have had symptoms for at least health care provider will take a medical 6 months and meet the following criteria for history, perform a physical exam, and order the last 3 months before diagnosis:3 specifc tests. The blood test can show how long symptoms have been present, if there may be an underlying disease or frequency of bowel movements, consistency condition causing constipation. Physical Exam the health care provider may give the person A physical exam should include a rectal exam written bowel prep instructions to follow at with a gloved, lubricated fnger to evaluate home. An enema involves the health care provider may perform a fushing water or laxative into the anus using test for blood in the stool by placing a small a special squirt bottle. The large intestine Additional testing is usually reserved is flled with barium, a chalky liquid, making for older adults and people with severe signs of problems that may be causing symptoms, sudden changes in the number constipation show up more clearly on x rays. Additional tests that may For several days, traces of barium in the be used to evaluate constipation include large intestine cause stools to be white or light colored. These tests show tests are similar, but a colonoscopy is used how well food moves through the colon. With this a fexible sigmoidoscopy is used to view just technique, the person swallows capsules the rectum and lower colon. These tests containing small markers that are are performed at a hospital or an outpatient visible on an x ray. For both waste do and are passed naturally with tests, a health care provider will give written stool. One or more enemas several times, monitor the movement may also be required the night before and of the markers through the colon. This type of nuclear gastroenterologist inserts a fexible tube into medicine study relies on the detection the anus. A small camera on the tube sends of small amounts of radiation after a video image of the intestinal lining to a a person eats a meal containing computer screen. Special external cameras and a small piece of intestinal lining tissue for computers are used to create images of examination with a microscope. Driving is an outpatient procedure by a specially not permitted for 24 hours after a fexible trained technician, and a radiologist sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy to allow interprets the results. Full recovery is expected by the diagnose constipation caused by anorectal next day. To prepare for these 6 Constipation tests, the person should use an enema and toilet inside an x-ray machine. The radiologist studies the x rays and a balloon that can be infated in for anorectal problems that occurred as the the rectum to check the sensitivity paste was expelled. Anal manometry also checks the tightness of the anal sphincter muscles around How is constipation treated The person is given a changes in eating, diet, and nutrition; stopwatch and instructed to go to the exercise and lifestyle changes; and laxatives. If the treatments should talk with their health care person cannot expel a balloon flled with provider about other treatments. Americans consume area shows how well the person can hold only 15 grams a day on average. The test also identifes often eat too many refned and processed structural changes in the rectum and anus, foods from which the natural fber has been such as rectocele and rectal prolapse. A health care provider can help Rectocele is a condition in which the rectum plan a diet with the appropriate amount of protrudes through the vagina, and rectal fber. A list of high-fber foods is shown on prolapse is a condition in which the rectum page 8. To prepare limit foods that have little or no fber, such as for the test, the person uses two enemas ice cream, cheese, meat, and processed foods. Position of the American Dietetic that shows up on x rays and is the same Association: health implications of dietary fber. Drinking water and other liquids, such as Exercise and Lifestyle Changes fruit and vegetable juices and clear soups, Engaging in daily exercise can help people may make fber in the diet more effective in with constipation. Another strategy is normalizing bowel function and maintaining to try to have a bowel movement at the regularity. Stool softeners may be suggested for people who should When a medication is causing constipation, avoid straining in order to pass a the health care provider may suggest the bowel movement; they are often person stop taking the medication or switch recommended after childbirth or to a different medication. Lubricants work diet and lifestyle changes and are still by coating the surface of stool, which constipated. Laxatives taken by mouth helps the stool hold in fuid and pass are available in liquid, tablet, powder, and more easily. Brand names recommended for people with anorectal include Metamucil, FiberCon, Citrucel, blockage. Brand names include trigger the bowel to contract and push Correctol, Dulcolax, Purge, and stool out. Stimulant laxatives cause be taken with water or they can cause the intestines to contract, which moves obstruction. Stimulants should be reserved are generally considered the safest for constipation that is severe or has laxative, but they can interfere with the not responded to other treatments. Many People should not use stimulant people also report no relief after taking laxatives containing phenolphthalein, bulk-forming agents and suffer from as phenolphthalein may increase the bloating and abdominal pain. Osmotic agents help stool retain Lubiprostone (Amitiza) is a chloride fuid, increasing the number of bowel channel activator available with a movements and softening the stool. Treatment for hemorrhoids may include making dietary changes to prevent Surgery may be needed to correct an constipation, taking warm tub baths, and anorectal blockage caused by rectal prolapse. Anal fssures are small tears in the anus that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Biofeedback Treatment for anal fssures may include People with chronic constipation caused making dietary changes to prevent by problems with the anorectal muscles constipation, applying cream to numb can use biofeedback to retrain the muscles. The measurements are fssures that do not respond to at-home displayed on a video screen as line graphs treatment can be treated with minor surgery. The condition provider uses the information to help the may lead to mucus leaking from the anus. The person such as straining or coughing, is usually the may need to continue practicing for 3 months only treatment needed. Fecal impaction occurs when hard stool Sometimes constipation can lead to packs the intestine and rectum so tightly complications, such as hemorrhoids, anal that the normal pushing action of the colon fssures, rectal prolapse, and fecal impaction. This condition occurs most often in children and Hemorrhoids are swollen and infamed older adults. An impaction can be softened veins around the anus or in the lower with mineral oil taken by mouth or through rectum that can be caused by straining an enema. People with the health care provider may break up hemorrhoids may have rectal bleeding that and remove part of the hardened stool by appears bright red on the surface of stool, inserting one or two fngers into the anus. Most effective new ways to prevent, detect, or constipation is acute and not treat disease. When prepared, this publication included the most current information National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive available. Established in 1980, the Clearinghouse provides information about digestive diseases to people with digestive disorders and to their families, the U. If a product is not mentioned, the omission does not with professional and patient organizations mean or imply that the product is unsatisfactory. The Clearinghouse encourages users of this publication to duplicate and distribute as many copies as desired. The trend varied with more than 265, 000 hysterectomies performed annually in the depending on whether an inpatient setting. Oophorectomy is a surgical procedure that removes one or both the rate of oophorectomy alone ovaries. Elective oophorectomy is routinely offered to older women at the time of hysterectomy to prevent the development of ovarian In five States in 2013, 26, 400 cancer. Procedures to Treat Benign most common conditions related Uterine Fibroids in Hospital Inpatient and Hospital-Based Ambulatory Surgery Settings, 2013. Trends in inpatient and outpatient related to the surgery, women hysterectomy and oophorectomy rates among commercially insured women in the aged 55 years and older were United States, 2000-2014. The distribution in 2013 of surgeries performed by related condition and by age is also provided. Number and distribution of hysterectomy and oophorectomy surgeries by hospital setting, in five States, 2013 Inpatient surgery Hospital-based ambulatory surgery 30, 000 25, 000 47. Of 65, 900 hospital visits involving hysterectomy, oophorectomy, or both in combination in 2013, 27, 000 hospital visits involved only a hysterectomy (41. Hospital-based operations for hysterectomy alone or oophorectomy alone were performed more frequently in the outpatient setting (69. Patient and hospital characteristics related to hysterectomy and oophorectomy surgeries, 2013 Table 1 presents characteristics related to hysterectomy and oophorectomy surgeries comparing surgeries performed in the hospital inpatient setting with those performed in the hospital-based ambulatory surgery setting in 2013. Patient characteristics and outcomes related to hysterectomy and oophorectomy surgeries by setting, in five States, 2013 Hysterectomy and Hysterectomy Oophorectomy oophorectomy in alone alone combination Characteristics Hospital Hospital Hospital Inpatient based Inpatient based Inpatient based surgery ambulatory surgery ambulatory surgery ambulatory surgery surgery surgery Patient characteristics Age, mean years 44.
Trusted rhinocort 100 mcg. Pollen Allergy Season in Japan Japanology.
References
- Kowey PR, et al. Randomized double-blind comparison of intravenous amiodarone and bretylium in the treatment of patients with recurrent, hemodynamically destabilizing ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation. The Intravenous Amiodarone Multicenter Investigators Group. Circulation 1995;92:3255-3263.
- Pierorazio PM, Hyams ES, Tsai S, et al: Multiphasic enhancement patterns of small renal masses (/= Bosniak category IIF), Urol Oncol 32(1):24 e1n24 e7, 2014.
- Travis WD, Colby TV, Corrin B, Shimosato Y, Brambilla E. Histological Typing of Lung and Pleural Tumours, 3rd ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1999.
- Hill EE, et al. Infective endocarditis: changing epidemiology and predictors of 6-month mortality: a prospective cohort study. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:196.
- Pavlakis PP, Alexopoulos H, Kosmidis ML, et al. Peripheral neuropathies in Sjogren syndrome: A new reappraisal. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2011;82:798-802.
- Liu Y, Hudetz AG, Knaus HG, et al. Increased expression of Ca2+- sensitive K+ channels in the cerebral microcirculation of genetically hypertensive rats: evidence for their protection against cerebral vasospasm. Circ Res 1998;82:729-37.
- Patel PH, Senico PL, Curiel RE, et al: Phase I study combining treatment with temsirolimus and sunitinib malate in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma, Clin Genitourin Cancer 7:24n27, 2009.
- Attal M, Harousseau JLLeyvraz S, et al. Maintenance therapy with thalidomide improves survival in multiple myeloma patients. Blood 2006;108(10):3289-94.