Oladipo A. Kukoyi, MD, MS
- Assistant Clinical Professor, UC Davis
- Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences
- Medical Director of Inpatient Psychiatry
- VA Sacramento Medical Center
- Hospital Way, Mather, California
Know the forms and appropriate dosages of androgens for treatment of constitutional delay of growth b erectile dysfunction treatment yoga buy 160mg malegra fxt plus mastercard. Know the effects of pubertal delay on growth erectile dysfunction pills from india discount malegra fxt plus 160mg line, adult height diabetes and erectile dysfunction health discount malegra fxt plus online master card, and skeletal maturation 2 erectile dysfunction in young guys purchase 160mg malegra fxt plus mastercard. Know the appropriate therapy and indications for hormonal treatment for familial tall stature 2 erectile dysfunction kits buy malegra fxt plus 160mg without prescription. Understand the value versus limitations/risks regarding the use of estrogen therapy in girls with tall stature a erectile dysfunction doctor lexington ky cheap malegra fxt plus uk. Understand the rationale for and approaches to growth restriction therapy in specific situations E. Know that successful therapy depends on behavior modification leading to diminished food intake and increased activity b. Be familiar with the factors thought to be involved in the development of exogenous obesity d. Know the indications for and expected outcomes of surgical treatment of obesity in children and adolescents 2. Know the clinical and laboratory methods used to distinguish exogenous from endocrine obesity b. Know the growth pattern in obesity caused by hypothalamic tumors and their treatment c. Be familiar with syndromes of which obesity is part such as Prader-Willi and Bardet-Biedel 2. Know the genetics of Prader-Willi syndrome and its relationship to Angelman syndrome 3. Know the effect of obesity on cortisol secretion and measures to assess adrenocortical status c. Know the risk of patients with obesity for the development of diabetes mellitus. Know the risk of patients with obesity for the development of sleep apnea and pulmonary hypertension f. Be able to recognize the symptoms and signs of pulmonary complications in an obese adolescent g. Know that obesity in children is a risk factor for metabolic-insulin resistance syndrome h. Know that obesity increases the risk of Blount disease and of slipped capital femoral epiphyses i. Know that obesity increases the risk of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) 4. Understand the role of leptin in the control of pubertal onset in boys and girls 5. Understand the role of the regional distribution of body fat on serum leptin concentration b. Know that ghrelin stimulates the hypothalamus to direct an increase in energy production. Know the role of melanocortin receptor mutations in the pathogenesis of severe obesity F. Recognize that anorexia nervosa is considered to be primarily a psychiatric disease with serious endocrine and metabolic consequences and approximately 15% mortality b. Know the sequence of endocrine changes that result from weight regain in anorexia nervosa. Know that treatment of anorexia nervosa is primarily psychologic counseling and behavioral modification coupled with nutritional rehabilitation f. Know the appropriate therapy of the decreased bone mineral concentration associated with anorexia nervosa h. Know that ballet dancers, wrestlers, and long distance runners are at increased risk for eating disorders j. Know the components, diagnostic criteria, and treatment of the female athlete triad 2. Be familiar with the pathophysiology of bulimia and the effects of laxatives and diuretics in these patients b. Know that bulimia nervosa is commonly associated with impaired growth and undermineralization of bone in adolescents 7. Understand the mechanism and genetic regulation of the differentiation and growth of external genitalia in the fetus including the tissues of origin 2. Know the role(s) of key genes on the X and Y chromosomes for gonadal differentiation 5. Know the gene maps of the X and Y chromosomes and relationships between genes on the respective chromosome 6. Understand that germ cells migrate to the urogenital ridge to form the undifferentiated gonad b. Know the relationship of egg meiotic phases to ovulation and the developmental stages at which the phases are reached b. Know that two X-chromosomes are necessary for maintenance of primordial follicle c. Know the changes in the number, size, and composition of ovarian follicles with age d. Know the hormonal determinants of antral follicle formation and follicular growth. Know the determinants of spermatogenesis and the developmental stages at which various phases are reached b. Know the hormonal regulation of Leydig cell steroidogenesis and the rate limiting steps d. Know the steps of testicular differentiation and the developmental ages at which they are reached 4. Know the pros and cons of chorionic gonadotropin or gonadotropin analog treatment of cryptorchidism and the age at which it may be indicated d. Know the pros and cons of surgical treatment of cryptorchidism and the age at which it is indicated. Know the role of measuring testicular products in the diagnosis of cryptorchidism versus anorchia g. Know that the contralateral testis in a patient with an undescended testis might itself be abnormal h. Recognize how compensatory hypertrophy in a testis relates to the function of the other testis i. Know that cryptorchidism may lead to testicular carcinoma, the relative incidence of such carcinoma, and recommend monitoring c. Know that the Mullerian duct differentiates to the uterus, fallopian tubes, and upper vagina 3. Understand the paracrine actions of anti-Mullerian hormone during male reproductive development and the time at which it occurs d. Know the paracrine role of testosterone in normal and abnormal Wolffian duct differentiation b. Know that the Wolffian ducts differentiate into the rete testis, efferent ducts, epididymis, vas deferens, and seminal vesicle 2. Know the role of testosterone and dihydrotestosterone in pubertal development of the Wolffian derivatives. Know the embryonic precursors of the male and female external genitalia and the mechanism and timing of their differentiation 2. Know the role of dihydrotestosterone in the differentiation of male external genitalia f. Know the effects of androgens on the pilosebaceous unit on the scalp versus in the pubic and axillary area 2. Understand the physiologic and clinical importance of free (unbound) sex steroid hormone concentrations b. Know the organs that produce testosterone in men and women and the relative proportion secreted by each organ 2. Know the relative roles of secretion and peripheral metabolism in the production of testosterone in men and women 3. Know the structure and function of the androgen receptor and the steroids to which they respond 9. Know patterns of fetal concentrations of estrogens, progestins, androgens, and gonadotropins b. Know the organs that secrete estradiol in males and females and the relative proportion secreted by each organ 3. Know the role of secretion relative to peripheral metabolism in production of estradiol in men and women 4. Know the intracellular signaling pathway of estrogen action within target cells 7. Know the relationship of progesterone secretion to granulosa cell luteinization 2. Know the relative androgenicity of the synthetic progestins used in oral contraceptives d. Know the secretion of androstenedione relative to testosterone by the interstitial cells of ovaries and testes 2. Know the relative contribution of the peripheral metabolism of androstenedione to the synthesis of testosterone and estrone. Know the control of anti-Mullerian hormone and changes in concentrations throughout development c. Know the control of inhibin/activin secretion and changes in concentration throughout development c. Know that genetic determinants for stature and ovarian development are coded by different genes on the X-chromosome 2. Know the different karyotypes that can lead to Turner syndrome and the resulting clinical features 4. Know the risk of malignant degeneration of gonads in patients with gonadal dysgenesis and Y chromosomal material and the methods of identifying Y material 5. Know the pattern of gonadotropin secretion in gonadal dysgenesis as a function of age in girls and the reason that it differs from a normal girl c. Know the time course of changes in ovarian morphology in the development of ovarian failure, including the decline in ovum at various stages 2. Know the typical linear growth pattern of children with Turner syndrome in the fetus and after birth 3. Know the congenital cardiovascular abnormalities of girls with Turner syndrome and contrast them with Noonan syndrome 4. Know the increased incidence of autoimmune thyroiditis, celiac disease, and type 1 diabetes in children with Turner syndrome 5. Recognize the changes in the skeleton, including limb and vertebral abnormalities, in Turner syndrome that can be observed on x-ray studies 6. Know that Madelung deformity of the wrist occurs in some individuals with Turner syndrome 7. Recognize the cytogenetic findings that are associated with cognitive impairment in girls with Turner syndrome 9. Understand the behavior and psychologic problems that can be present in girls with Turner syndrome d. Know the pros and cons of estrogen therapy with different estrogen preparations in Turner syndrome including relative dosage and age of initiation of therapy 4. Know the outcome of growth hormone, estrogen and androgen therapy for Turner syndrome on metabolic changes and physical development 2. Know the pros and cons of treatment of Klinefelter syndrome with testosterone, including relative dosage and age of initiation of therapy f. Know that individuals with Klinefelter syndrome are at increased risk for germ cell tumors, what types, and where they are located i. Know the relative risk of breast cancer is increased in individuals with Klinefelter syndrome b. Know the principles underlying sex assignment in individuals with genital ambiguity 2. Recognize the relative risks for malignancy in different disorders of gonadal development 3. Understand the correlation between the genital phenotype and the timing of inadequate androgen secretion or action during sex differentiation 3. Know the different syndromes resulting from embryonic or fetal testicular dysgenesis at various times between 8 to 40 weeks gestation 4. Understand how to recognize and diagnose the genetic defects in testosterone and dihydrotestosterone synthesis 6. Differentiate the clinical and genetic features of androgen receptor defects from alpha-reductase deficiency 7. Know the heredity of testicular enzyme defects, androgen insensitivity, and 5 alpha-reductase deficiency 8. Understand the effects of untreated testosterone biosynthetic defects, androgen insensitivity syndromes, and 5 alpha-reductase deficiency on pubertal sexual development 10. Know how to distinguish virilizing congenital adrenal hyperplasia as a cause of virilization from placental aromatase deficiency and maternal causes (luteoma, exogenous adrongens) 3. Know the types of hormones and medications ingested by the mother that might cause fetal virilization 5. Be aware of disorders of embryonic development that result in genital abnormalities b. Know the role of diethylstilbestrol in abnormal Mullerian epithelium development in subsequent generations 2. Know that micropenis may result from hypopituitarism or primary defects in testosterone secretion or action 2. Recognize that micropenis may be associated with other hormonal deficiencies resulting in hypoglycemia and nystagmus 3.
Online doctors appointments are likely to 23 appeal to many people who are already acclimated to the use of apps to fulfill personal needs impotence vitamins cheap malegra fxt plus line. However erectile dysfunction drug warnings discount malegra fxt plus 160 mg on-line, the potential dangers of sharing personal health information over such networked connections is a concern impotence klonopin cheap malegra fxt plus 160mg with visa. In 2016 best erectile dysfunction pills review order malegra fxt plus once a day, DeepMind launched several initiatives in the health care arena under its DeepMind Health Division [67] erectile dysfunction gif generic malegra fxt plus 160 mg on line. For example erectile dysfunction and diabetes type 2 purchase malegra fxt plus 160mg on-line, the problem discussed above with data access transparency may have led DeepMind to an accelerated application of blockchain-style technology for securing and tracking data access [72]. Basically, blockchain methodologies use a distributed database consisting of continuously updated (augmented) blocks which contain a linked list of all previous transactions [73]. In the case of health care, this encompasses all previous records of access to an individual data record including information about how the data was used and any additions or changes to the data record [74,75]. A second technology application that has emerged from DeepMind Health has many blockchainlike aspects [76,77]. Instead of blockchain, the DeepMind data audit system uses an approach based on Merkle Trees [78], a type of hash tree that allows secure verification of the contents of large data structures. DeepMind hopes to prototype the verifiable data audit system by the end of 2017 for eventual use in its Royal Hospital health care software environment [79]. Findings: Revolutionary changes in health and health care are already beginning in the use of smart devices to monitor individual health. This will promote the entry of all sorts of companies into this space, both meritorious and not. For instance, there are already many paid online services available that will help people interpret their Ancestry. This well studied gene has also been associated with numerous ills including contributing to plaque formation by damaging arterial walls and increasing the risks of clot formation. Here is a genetic variant that millions have been tested for (often inadvertently, via ancestry genetic testing) that sounds pretty scary. According to an expose, [81] in one case the consultation costs $3000, and generally results in a prescription of exotic vitamin combinations only available through the site. Computer-aided automated skin cancer detection was demonstrated on biopsy-proven clinical images and tested against 21 dermatologists [82]. In parallel, online services already exist for remote dermatologist diagnosis of online-submitted images of skin moles [83]. We could imagine a scam service asking patients to submit self-taken skin mole images along with payment for an automated quack diagnosis in return, one that did not actually use any validated classification scheme. More likely, the methods used by any one company may be hidden or obscure, meaning the user has no way to judge the soundness of the company. Skinvision [83] is a new company based in the Netherlands for skin cancer melanoma detection where users download an app, take a picture for the app, and receive analysis, diagnosis, and tracking by the app. Very little information is provided about the methods used, other than Skinvision uses the mathematical theory of fractal geometry for medical imaging to diagnose suspected melanoma and that the algorithm has been developed and tested in cooperation with dermatologists and checks for irregularities in color, texture, and shape of the lesion, although elsewhere in fine print the website acknowledges that our solution is not a diagnostic device. The threat of bogus web sites is diminished in the presence of trusted, credible resources. For example, information about cancer symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options are provided by the American Cancer Society [84] and the Mayo Clinic [85]. It has been tremendously successful as a provider of news and information related to human health and well-being. Addressing this inevitable train wreck before it happens leads us to the following finding and recommendation. Websites, apps, and companies have already emerged that appear questionable based on information available. First is access to a smart platform such as a smartphone, and the second is access to the useful apps and devices. Recent data (2016) from Pew Research Center indicate 95% of Americans own a cellphone of some kind and 77% actually own a smartphone [87]. This is a sharp charge from 2011 where 83% of Americans owned a cellphone of some kind and only 35% owned a smartphone [88]. The distributions of cellphone and smartphone ownership for 2016 are given in Table 3. Ownership rates among men and women and different racial groups are quite similar. There are some differences across income and education levels, but overall rates are higher for every group than in 2011. The elderly have lower adoption with only 80% of the 65+ age group owning a cellphone and only 42% owning a smartphone in 2016. Nonetheless, adoption is growing for the elderly as only 46% owned any sort of cellphone in 2011 and only 11% owned a smartphone. A Pew report from 2015 [89] pointed out that a growing number of Americans are using their smartphone as their primary broadband access device, with the largest groups with the behavior being non-white with lower education and income levels. It was also noted that more than half of all smartphone owners used their devices to access health information and do on-line banking. However, there may be inequitable differences among these demographic groups in the means, education levels, or physical capabilities needed to purchase, understand or use the tools. There are many issues of being able to develop and share datasets based on health and health care data. Other issues include the fact that the data may contain sensitive information about real people. Additionally, the culture in biology and life sciences, to include health care, is to closely protect ones data that has typically been expensive and time intensive to collect. Few incentives exist to share this data until the primary researchers have squeezed all the results they can from their data. But first, there are overarching findings and recommendations associated with expanding the availability and access to comprehensive databases of health data. Several of the examples made use of the highly successful 29 ImageNet competition [92] results to initiate their deep learning algorithms. The two specific vehicles for this are crowdsourcing via online technical competitions and citizen science via online public engagement activities. The crowdsourcing competitions are able to engage top data scientists and programmers who are not health care domain experts. Some competitions have seen thousands of participants while others are purposefully limited to a select group of dozens of invited participants chosen from a pool of prior successful competitors. Monetary prizes are often given out to the top winners, and from typical totals as small as $10K through $100K even up to $1M. Leaderboards serve to motivate the competitors and discussion boards promote sharing of information sometimes leading up to collaborations in the competitions themselves. Contributed code is usually made public and serves both as a benchmark and to move the field forward. Crowdsourcing is motivated by the fact that while there are numerous and varied strategies that can be applied to any predictive modeling task, it is impossible to know at the outset which technique will be most effective. Kaggle [93] is a popular, successful, and leading online data science competition host with over 760,000 members around the world and hundreds of completed competitions in a variety of fields. One of the most successful health competitions to date was held in 2016-2017, run by Kaggle and Data Science Bowl [94] with support from over two dozen organizations. Competitors used anonymized, high-resolution lung scans from hundreds of patients provided by the National Cancer Institute. But the challenge is distinguishing the mutations that contribute to tumor growth (drivers) from the neutral mutations (passengers). This is a very timeconsuming task where a clinical pathologist has to manually review and classify every single genetic mutation based on evidence from text-based clinical literature. We need your help to develop a Machine Learning algorithm that, using this knowledge base as a baseline, automatically classifies genetic variations. The main challenge for crowdsourcing efforts is the required large, well-labeled public or semipublic datasets in order to get the proper community involvement. Nobody could have predicted the benefits that derived from the careful creation of the ImageNet database [99], and we conjecture that the expanded creation of similar high-quality databases for health data could also lead to unforeseen advances. There are already websites that are perfectly positioned to host such competitions, such as Kaggle [94]. A second major challenge to online competitions is in how to move competition-resulting software to clinical tools. One unique feature of this competition over some of the data-analysis-only competitions is that it will require creating teams of data scientists, software engineers, designers, and clinicians working together. A third major challenge is that competitions, thus far, are mostly limited to image recognition/computer vision. Complex and heterogeneous datasets, noisy medical datasets are not yet addressed (see Section 6. Yet, in contrast, large data-gathering projects (like the All of Us Research Program, see Section 5. Data fusion, the integration of multiple heterogeneous data sources, is an example suggestion for a new type of contest. Health data has features that make it unique from all other types of data, and contests could be designed to facilitate an understanding of what those features are, and how to correct for them. One example could be giving participants access to both electronic health records and billing data for a collection of patients that would require creative data linkage strategies to develop matched data and corresponding analyses. Citizen Science is a form of collaboration where members of the public participate in scientific research, a paradigm where the activities of an engaged public are intertwined with professional scientific research. One recent medical-related citizen science example is on bacterial resistance to antibiotics [102]. Understanding which changes in 31 the bacterial genome (mutations) lead to antibiotic resistance enables the identification of which antibiotics can be used to treat a particular patient, in a week rather than current practice of a month. Each sample will have its genome sequenced and for each sample the volunteers will help determine the samples sensitivity to a range of antibiotics based on images of plates with different antibiotic doses where bacteria have been allowed to grow. Volunteers are simply asked to view images of plates and identify whether or not bacteria are growing. Here the hosts aim to compare and combine inputs by the volunteers, expert opinion, and computer processing of images to get an accurate assessment of each plate. Public forums are needed to engage citizen scientists in helping find new discoveries that will benefit health and wellness. The creation of discovery-based challenges that build on crowdsourcing and citizen science lessons learned from other areas of science and engineering. However, various techniques are in fact known for utilizing deep learning in contexts where labeled data are unavailable or impractical. Three worth mentioning are reinforcement learning, auto-encoders, and generative adversarial networks. In reinforcement learning, typically, the input to a deep neural net is a complex image or feature set, while the output is supposed to be a set of policies that maximize a score. To train the net, we must provide an algorithm that evaluates and scores the output policies. In an early successful example, the input images were the continuous screenshots of the Atari game Pong, while the output policies were joystick moves that the computer makes. The score in this case is simply the Atari score displayed on the screen (which, in effect, the computer learns to read). So, in this example, as a substitute for labeled data, the computer simply plays the game many millions of times. Auto-encoders provide a methodology for autonomously learning to summarize a complex input signal (an image, for example) in terms of a small(er) number of features. The decoder side starts with these features and attempts to re-synthesize the original complex input. The training goal is to maximize the fidelity of the output image, as compared to the input image, after passing through the narrow neck of the feature vector. Once it is trained, we can use the auto-encoder in real time in two ways: It can produce feature vector output from complex input. As a notional example in health care, we might use an auto-encoder to learn how to do differential diagnosis, where the small number of features at the narrow neck are the diagnoses, while the complex input (and synthesized output) are the continuous signals of heart monitors, etc. In generative adversarial networks (or other similar adversarial networks) we allow two deep neural nets to play against each other, so that each becomes good at countering the behavior of the other. In a symmetric example, the two networks could be players in a two-person game. Playing against itself (actually an independent copy of itself), the network learns to become a good Go player. In asymmetric examples, one network is often termed generative, the other discriminative. The job of the generative network is to generate images (say) that fool the discriminative network, while the job of the discriminative network is not to be fooled. As the two networks play against each other, both networks improve, leading to a trained discriminative network. One new application of the use of these networks in health is to generate simulated or synthetic electronic health records that carry the same properties as the original data, thus purportedly preserving the privacy of the subjects [105]. Finding: Techniques for learning from unlabelled data could be helpful in addressing the issues with using data from a diverse set of sources, such as those discussed in Section 3. It is estimated that 60% of premature deaths [106] are accounted for by social circumstances, environmental exposures, and behavioral patterns [107]. These three areas are a combination of experiences throughout our life based on where we were born, live, learn, work, and play.
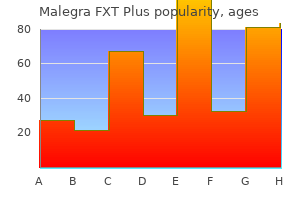
Although the groups received the same regimen of methylprednisolone strength of supportive data is low (retrospective case series 1000 mg i erectile dysfunction fruit order malegra fxt plus 160 mg without prescription. Whether patients with mild alveolar with cyclophosphamide) impotence from priapism surgery purchase discount malegra fxt plus on line, as were rates of serious adverse hemorrhage (small focal inltrate without or with mild 713 events impotence hypothyroidism generic malegra fxt plus 160 mg otc. Although small justied in patients at high risk of relapse erectile dysfunction new drug buy malegra fxt plus 160 mg free shipping, but the potential uncontrolled studies report remission rates similar to those benet of maintenance therapy may be low in patients who 720 reported with corticosteroids and cyclophosphamide erectile dysfunction 9 code buy 160 mg malegra fxt plus otc, have a low likelihood of relapse erectile dysfunction treatment by exercise 160mg malegra fxt plus with visa. No data K There is low-quality evidence that the duration of on follow-up beyond 6 months is provided in this study. The indications for maintenance therapy are not well the risk-benet ratio of maintenance therapy has not been dened. The study was not (1C) designed to demonstrate the superiority of methotrexate over 13. Examples of life-threatening relapse include diffuse we recommend the addition of rituximab alveolar hemorrhage and severe subglottic stenosis. In patients with kidney dysfunction, it is preferable to use a sucrose-free formulation of i. Although treatment regimens were designed to remove the circulating mortality has improved, kidney survival remains poor, pathogenic antibody that caused the disease, suppress further possibly because of delays in making the diagnosis and synthesis of this pathogenic antibody, and attenuate the initiating treatment. The most optimistic study observed that all tion, patient and kidney survival were reduced to 65% and patients with a combination of dialysis at presentation plus 8% at 1 year, and 44% and 13% at 5 years, respectively. A survey of hemorrhage and kidney failure in historical series, this several studies shows dialysis dependence at diagnosis in a treatment strategy represented a signicant improvement. After topics and relevant clinical questions based at the Tufts Center for Kidney Disease Guideline were identied, the pertinent scientic literature on those Development and Implementation at Tufts Medical Center in topics was systematically searched and summarized. The rst task of the Work Group was to dene the overall K Assign topics to systematic review or narrative review. The Work Group K Define specific populations, interventions or predictors, Co-Chairs drafted a preliminary list of topics. Group identied the key clinical questions and triaged topics K Create and standardize quality assessment methods. The outcomes were the inclusive, combined set of questions formed the basis for further categorized as being of critical, high, or moderate the deliberation and discussion that followed. The specic criteria Group aimed to ensure that all topics deemed clinically used for each topic are described below in the description relevant and worthy of review were identied and addressed. For most topics, the minimum duration of follow-up of Table 34 Hierarchy of outcomes 6 months was chosen based on clinical reasoning. The lists are not meant to reflect outcome ranking for other areas Included were studies of all patients with glomerular of kidney disease management. If these reviews were deemed to adequately the study size, country of residence, and baseline kidney address topics of interest (even if only selected outcomes were function and proteinuria. The studies were the time period since the end of literature search within the listed by outcome within the table, based on the hierarchy of systematic reviews. Similarly, longer-duration studies may be of better to tabulate information on various aspects of the primary quality and more applicable, depending on other factors. The quality of a body of evidence refers to the extent to which our study quality was used (Table 35). Given the potential condence in an estimate of effect is sufficient to support a 760 differences in quality of a study for its primary and other particular recommendation. The calculated data were distinguished from No100), or if there was thought to be a high likelihood of the reported data in the summary tables. The quality of grading for topics relying on reader the thinking process of the Work Group in systemsystematic reviews are based on quality items recorded in the atically combining evidence and judgments. Decisions Grading the overall quality of evidence: the quality of the were based on facts and ndings from the primary studies overall body of evidence was then determined based on the listed in corresponding summary tables, as well as selected quality grades for all outcomes of interest, taking into existing systematic reviews, and judgments of the Work account explicit judgments about the relative importance of Group. Grading evidence and recommendations for clinical practice guidelines in nephrology. Each section contains one ungraded statement meets the following criteria: it provides or more specic recommendations. Table 40 Determinants of strength of recommendation Factor Comment Balance between desirable the larger the difference between the desirable and undesirable effects, the more likely a strong recommendation and undesirable effects is warranted. Values and preferences the more variability in values and preferences, or more uncertainty in values and preferences, the more likely a weak recommendation is warranted. Where randomized trials declarative sentences summarizing the key points of the were lacking, it was deemed to be sufficiently unlikely that evidence base, and the judgments supporting the recomstudies previously unknown to the Work Group would result mendation. This is followed by a narrative in support of the in higher-quality level 1 recommendations. In relevant sections, research recommendations suggest future research to resolve current uncertainties. Institute of Medicine standards, and how each one of them is Not all topics and subtopics covered by these guidelines could addressed in this guideline. He has also held a number of Committee; and Renal Association International Committee. His primary research interest lies in and brosis in the course of renal disease) as well as clinical the area of parenchymal renal disease with a focus on the problems such as immune-mediated renal disease, bone and glomerulopathies. He is also the Honorary Professor of Medicine at Board of Directors/Advisory Board: American Renal Associthe Chinese University of Hong Kong. He was Cochrane Collaborations Renal Review Group, which is also the Scientic Vice-President and Program Chair for the based in the Centre for Kidney Research at the Childrens 2nd Congress of the International Society for Hemodialysis Hospital at Westmead. Jha has authored over 160 publications and Advisor/Consultant: Baxter Healthcare 25 book chapters, and serves as an editor of an upcoming Speaker: Baxter Healthcare; Fresenius; Roche textbook, Management of Kidney Transplant Recipient. In 2003, she was also including the participation of a number of clinical trials for elected as Academician in Chinese Academy of Engineering. She has published 390 postgraduate education both at the national and internaarticles, authored two books, and contributed chapters to tional level. Liu directs one of the most productive renal patient completed a nephrology fellowship at Hospital Puerta de care and research programs in China, the Research Institute Hierro, Madrid, Spain. He undertook his Who Among Americas Teachers & Educators and Americas training in Internal Medicine and Nephrology at the Best Doctors. Subsequently, he continued his training in internal multiple editions of Americas Best Doctors since 2005. His major scientic interests are in Osprey; Questcor; Teijan Pharmaceuticals; Teva the molecular mechanisms and physiological/pathophysioloGrant/Research Support: Biogen Idec; Centocor; Genentech; gical relevance of oxygen sensing and the management of Questcor; Roche; Teva anemia. Professor Eckardt is Subject Editor of Nephrology Medicine at Universitede Montreal,Quebec, Canada and Dialysis Transplantation, and serves on the editorial board of nephrologist at Hopitaldu Sacre-Coeurde Montreal. Troyanov completed his medical studies at Universiteand most recently served as a Co-Editor of the text Studies on de Montrealand received fellowship training at University of Renal Disorders. Her primary research interests are Advisory Board of the National Kidney Foundation. He health technology assessment, systematic review and clinical is currently serving on the Board of Councilors of the practice guideline development. Her primary research interests are in comparative effectiveness research in dialysis Advisor/Consultant: Litholink patients, blood pressure treatment in dialysis patients, and Grant/Research Support: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Merckautosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Dr Deo was awarded a Master of Science in Practice Center, and Assistant Professor of Medicine at Tufts Clinical Research for her thesis on Loss to Analysis in University School of Medicine. Dr Balk graduated from Tufts Randomized Controlled Trials of Chronic Kidney Disease. University School of Medicine and completed a fellowship in Clinical Care Research. We are also especially grateful to the Work Lupo, Bruce Mackinnon, Patricia Delgado Mallen, Carmela Group members for their expertise throughout the entire Martorano, Claudio Mascheroni, Anton Maurer, Peter A process of literature review, data extraction, meeting McCullough, Alain Meyrier, Walid Ahmed Abdel Atty participation, the critical writing and editing of the Mohamed, Jose M Morales, Gabriella Moroni, Eugen Mota, statements and rationale, which made the publication of Michal Mysliwiec, Judit Nagy, Masaomi Nangaku, Bharat this guideline possible. Finally, and on behalf of the Matti Nuutinen, Suzanne Oparil, Antonello Pani, Rulan S Work Group, we gratefully acknowledge the careful assessParekh, Sonia Pasquali, Saime Paydas, Roberto Pecoits-Filho, ment of the draft guideline by external reviewers. The Work Patrick Peeters, Momir Polenakovic, Claudio Ponticelli, Group considered all of the valuable comments made and, Claudio Pozzi, Dwarakanathan Ranganathan, Troels Ring, where appropriate, suggested changes were incorporated into Michael V Rocco, Cibele Isaac Saad Rodrigues, Michael the nal publication. Alternate-day versus intermittent prednisone in frequently relapsing interpretation of the renal biopsy. A report of the International Study of Kidney Disease in rate: Cockcroft-Gault and Modification of Diet in Renal Disease formulas Children. Varicella vaccination in children with relapses in children with nephrotic syndrome. Remission of proteinuria in primary prednisolone during viral infections reduces the risk of relapse in glomerulonephritis: we know the goal but do we know the price Children with steroid-sensitive prednisolone therapy in frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome. Nephrotic syndrome in South proven, frequently relapsing minimal-change nephrotic syndrome in African children: changing perspectives over 20 years. High incidence of initial and late treatment for frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome in children. Cyclosporine-A-induced nephrotic syndrome on long-term cyclosporin and steroid treatment. Clinical trial of mycophenolate frequently relapsing minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Pharmacokinetics of enteric-coated chlorambucil plus prednisone in the idiopathic nephrotic syndrome of mycophenolate sodium in stable pediatric renal transplant recipients. Randomized double-blind placebo controlled, multi-center trial severe steroidor cyclosporine-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a of levamisole for children with frequently relapsing/steroid dependent multicentric series of 22 cases. Side effects of levamisole in children disease in adolescents with primary nephrotic syndrome. High serological response to cyclophosphamide for patients with steroid-dependent and frequently pneumococcal vaccine in nephrotic children at disease onset on highrelapsing idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: a multicentre randomized dose prednisone. Prevention of serious bacterial infection in focal glomerulosclerosis from the time of presentation. High absolute risks and serum C3 concentration in patients with idiopathic focal predictors of venous and arterial thromboembolic events in patients glomerulosclerosis. Adult minimal-change disease: chronic kidney disease in children and ddolescents: evaluation, clinical characteristics, treatment, and outcomes. Kidney Int 1986; 29: both familial and sporadic steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Long-term renal tolerance of mofetil in children with steroid/cyclophosphamide-resistant nephrotic cyclosporin A treatment in adult idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Mycophenolate mofetil therapy for syndrome-a randomized controlled multicentre trial by the childhood-onset steroid dependent nephrotic syndrome after long-term Arbeitsgemeinschaft fur Padiatrische Nephrologie. Changing incidence of dysfunction associated with minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Review on diagnosis and findings in individuals with nephrotic proteinuria according to serum treatment of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. The long-term prognosis of glomerulosclerosis: a preliminary uncontrolled study with prospective patients with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. M-type phospholipase A2 trial of cyclophosphamide, warfarin and dipyridamole in idiopathic receptor as target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. In: Ponticelli C, nephropathy and nephrotic syndrome: outcome in the era of evidenceGlassock R (eds). Membranous nephropathy: its relative methylprednisolone plus chlorambucil versus methylprednisolone plus benignity in women. Oral cyclophosphamide versus of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: its clinical and research chlorambucil in the treatment of patients with membranous implications. Comparison of the azathioprine in the nephrotic syndrome secondary to idiopathic influence of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor lisinopril and membranous glomerulonephritis. Treatment of idiopathic chlorambucil as compared with prednisolone alone for the treatment of membranous nephropathy unresponsive to methylprednisolone and idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Relapsing membranous treatment of nephrotic idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a nephropathy. Response to therapy of relapses compared to that of the multicenter randomized controlled trial. Collaborative Study of the Adult Idiopathic and persistent or relapsing disease activity. Nephrotic syndrome in children: prediction of histopathology from mofetil in idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a clinical trial with clinical and laboratory characteristics at time of diagnosis. Atlas of mycophenolate mofetil and prednisolone in the treatment of end-stage renal disease.
Knowledge and Skills for Speech-Language Pathologists With Respect to Evaluation and Treatment for Tracheoesophageal Puncture and Prosthesis impotence groups purchase malegra fxt plus 160mg fast delivery. Definition Developmental written language disorders are characterized as delays or deficiencies in the reading comprehension and written expression of language erectile dysfunction treatment singapore purchase malegra fxt plus 160mg overnight delivery. The impairment may involve difficulty understanding and expressing written information because of their preexisting problems in knowledge and use of spoken language (vocabulary erectile dysfunction protocol book download discount malegra fxt plus 160mg, grammar erectile dysfunction natural treatment options trusted 160mg malegra fxt plus, syntax and nonliteral language concepts) erectile dysfunction drug overdose malegra fxt plus 160mg overnight delivery. Reading and writing require the foundational spoken language skills of phonological processing erectile dysfunction needle injection discount malegra fxt plus 160mg on-line, vocabulary knowledge, spoken language comprehension and executive functioning. These disorders may manifest symptoms of dyslexia and/or dysgraphia, but diagnosis of dyslexia and/or dysgraphia alone do not qualify as a Developmental Written Language Disorder. Please note that the information contained in this guideline may be best understood in concurrence with the guideline for Spoken Language Disorders in Pediatrics. History Goals of Complaint History Identify co-morbidities affecting general management or require medical management. Page 229 of 245 Presentation A written language disorder presents as difficulty in understanding and expressing written information because pre-existing problems in knowledge and use of spoken language (vocabulary, grammar, syntax and non-literal language concepts). A prior or current diagnosis of spoken language disorder typically precedes the diagnosis of a written language disorder. Page 230 of 245 Scores on reading tests below normal Scores on Reading Tests below normal limits with difficulty noted in the following limits with difficulty noted in some or all of areas: the following areas: Impaired reading comprehension of oral or Difficulty with: silent reading for: Naming letters Words (vocabulary) Associating sounds with letters Sentences Storing written words in memory Text (factual & inferential questions) Impaired written composition: Impaired: Word retrieval (finding right word) Accuracy and/or rate for sounding out Morphology (grammar. May their sounds, poor sequencing of finger demonstrate dyslexia and/ or dysgraphia as movements in order to write letters with or well. If the performance measure falls more than 1 standard deviation below the mean more than one of the standardized tests battery a disorder is present. Page 232 of 245 Identify the communication demands in the home. Test Instruments for evaluating literacy skills Page 233 of 245 Diagnosis of a written language disorder includes assessment of spoken language skills as well. Please see a list of evaluative tools in the Pediatric Spoken Language Evaluation Guideline. If the performance measure falls 1 standard deviations below the mean on more than one standardized test, a child may be diagnosed with a written language disorder and/or clinicians description of behavioral observations as well as use of checklists to indicated disordered skills based upon age level of child, if the child is not a candidate for standardized testing. Page 234 of 245 Management the following management will vary depending on the specific needs of the child. Using a balanced focus allows the child to learn and participate within the context of authentic language uses while they participate in a variety of written communication situations within his/her home, school and/or community. Frequency and Duration Treatment frequency and duration must be based on: Severity of objective clinical findings, Presence of and number of complicating factors and comorbidities, Natural history and chronicity of condition, Page 235 of 245 Expectation for functional improvement with skilled intervention, Response to treatment provided Patients level of independence. Page 236 of 245 Treatment Plan Approaches and Options Click on link below to obtain further information on this topic. Treatment Plan Timeline Frequency and duration of services is based upon the specific needs of the child at the time of the evaluation. Children with written language disorders tend to have periods where they plateau then will go on to make functional improvements. Early Stages of Treatment Explore factors that could impact outcomes now and in the future Explore strengths and weaknesses, and other components for best treatment outcomes Explore family understanding, challenges, and capabilities to develop education and training program Develop treatment program based on findings and best practices for this patient Develop an individualized supplemental home program to monitor and change as needed Document findings, techniques and responses to treatment Ongoing Treatment Provide patient/family ongoing education and training Assess response to and feedback from home program to modify, and update Document measurable gains and modify plan of care if indicated Assess ongoing response to treatment, gains, lack of progress, other factors; modify program as needed Assess if intelligible verbalization or supplemental and/or alternative means of communication will be probable; develop these or refer as needed Determine other factors impacting condition requiring intervention or referral (see referral guidelines) Later Stage of Treatment/Discharge Planning Provide suggestions and resources for follow-up Provide home program to continue to progress and/or to maintain gains Page 238 of 245 Provide summary of course of treatment and progress If discharged due to medical issues and/or plateau in progress, indicate under what future conditions a new referral would be warranted Page 239 of 245 Discharge Criteria Medical/psychological or other issues interfering with goals of treatment program Insurance benefit has ended Goals have been reached Able to continue with a home management or other supplemental program Non-response to treatment justifies discharge Home Medical Equipment Augmentative and assistive communication device. Page 240 of 245 References 1. Reading disability defined as a discrepancy between listening and reading comprehension: A longitudinal study of stability, gender differences, and prevalence. Phonologic awareness: Implications for individuals with little or no functional speech. Preliminary evidence of widespread morphological variaitons of the brain in dyslexia. A longitudinal investigation of reading outcomes in children with language impairments. Evidence-based systematic review: Effects of different service delivery models on communication outcomes for elementary school-age children. Male prevalence for reading disability is found in a large sample of Black and White children free from ascertainment bias. Specific language impairment in families: Evidence for co-occurrence with reading impairments. Stepping Stones to Literacy: A prevention-oriented phonological awareness training program. Creative and stylistic devices employed by children during a storybook narrative task: A cross-cultural study. Teaching sound letter correspondence and consonant-vowel-consonant combinations to young children who use augmentative and alternative communication. Strategy use by good and poor comprehenders reading expository text of differing levels. Age of first bilingual language exposure as a new window into bilingual reading development. Comorbidity of reading and mathematics disabilities: Genetics and environmental etiologies. Using a repeated reading program to improve generalization of oral reading fluency. A summary of the reading comprehension research undertaken with students who are deaf or hard of hearing. Language disorders from infancy through adolescence: Listening, speaking, reading, writing, and communicating. Multicultural students with special language needs: Practical strategies for assessment and intervention. Prerequisite skills, early instruction and success in first grade: Selected results form a longitudinal study. General language performance measures in spoken and written narrative and expository discourse of school-age children with language learning disabilities. Cross-disciplinary dialogue about the nature of oral and written language problems in the context of developmental, academic, and phenotypic profiles. Matthew effects in reading: Some consequences of individual differences in the acquisition of literacy. Language disorders are learning disabilities: Challenges on the divergent and diverse paths to language learning disability. Avoiding the devastating downward spiral: the evidence that early intervention prevents reading failure. Language-related differences between discrepancydefined and non-discrepancy-defined poor readers: A longitudinal study of dyslexia in New Zealand. Effectiveness of a Spanish Intervention and an English Intervention for English Language Learners at Risk for Reading Problems. Identifying English language learners with learning disabilities: Key challenges and possible approaches. Matching student needs to instruction: Teaching reading and spelling using the Wilson Reading System. Study behavior as a function of metacognitive knowledge about critical task variables: An investigation of above average, average, and learning disabled readers. Materials appearing in this book prepared by individuals as part of their official duties as U. Printed in China Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data Manual of neonatal care / editors, John P. However, the authors, editors, and publisher are not responsible for errors or omissions or for any consequences from application of the information in this book and make no warranty, expressed or implied, with respect to the currency, completeness, or accuracy of the contents of the publication. Application of the information in a particular situation remains the professional responsibility of the practitioner. The authors, editors, and publisher have exerted every effort to ensure that drug selection and dosage set forth in this text are in accordance with current recommendations and practice at the time of publication. However, in view of ongoing research, changes in government regulations, and the constant ow of information relating to drug therapy and drug reactions, the reader is urged to check the package insert for each drug for any change in indications and dosage and for added warnings and precautions. Joselow Vice-Chair Social Worker Obstetrics and Gynecology Pediatric Advanced Care Team Boston Medical Center Childrens Hospital Boston and Dana-Farber Boston, Massachusetts Cancer Institute Joseph R. In addition, we welcome Anne Hansen from Harvard as a new editor and collaborator. In the Manual, we describe our current and practical approaches to evaluation and management of conditions encountered in the fetus and the newborn, as practiced in high volume clinical services that include contemporary prenatal and postnatal care of infants with routine, as well as complex medical and surgical problems. Although we base our practice on the best available evidence, we recognize that many areas of controversy exist, that there is often more than one approach to a problem, and that our knowledge continues to grow. Our commitment to values, including clinical excellence, multidisciplinary collaboration, teamwork, and family-centered care, is evident throughout the book. Support of families is reected in our chapters on Breastfeeding, Developmental Care, Bereavement, and Decision Making and Ethical Dilemmas. This would have been an impossible task without the administrative assistance of Jessica DeNaples and Katie Scarpelli. We also thank Nicole Walz, Sonya Seigafuse, and Ave McCracken of Lippincott Williams & Wilkins for their invaluable help. Nelson for their insights into newborn physiology and to Steward Clifford, William D. Cochran, John Hubbell, and Manning Sears for their contributions to the care of infants at the Boston Lying-In Hospital. We thank the former and current directors of the Newborn Medicine Program at Harvard: H. Mary Ellen Avery for her contributions to the care of infants all over the world and to the personal support and advice she has provided to so many, including the editors. Finally, we gratefully acknowledge the nurses, residents, fellows, parents, and babies who provide the inspiration for and measure the usefulness of the information contained in this volume. McElrath Assessment and Treatment in the Immediate Postnatal Period 5 Resuscitation in the Delivery Room 47 Steven A. Ringer 6 Birth Trauma 63 Elisa Abdulhayoglu 7 the High-Risk Newborn: Anticipation, Evaluation, Management, and Outcome 74 Vincent C. Smith 8 Assessment of the Newborn History and Physical Examination of the Newborn 91 Lise Johnson and William D. Ringer 14 Developmentally Supportive Care 166 Caroll Spruill Turnage and Lu-Ann Papile 15 Temperature Control 178 Kimberlee Chatson Follow-up Care of Very Preterm and Very Low 16 Birth Weight Infants 185 Jane E. Placencia Contents xvii Management of Neonatal End-of-Life Care 20 and Bereavement Follow-up 225 Caryn E. Douma Fluid Electrolytes Nutrition, Gastrointestinal, and Renal Issues Nutrition 230 21 Deirdre M. Anderson 22 Breastfeeding 263 Nancy Hurst Fluid and Electrolyte Management 269 23 Elizabeth G. Kienstra 38 Pulmonary Air Leak 446 Mohan Pammi 39 Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation 454 Gerhard K. Agrawal Cardiac Disorders 469 41 Stephanie Burns Wechsler and Gil Wernovsky Hematologic Disorders Blood Products Used in the Newborns 529 42 Steven R. Christou 46 Polycythemia 572 Deirdre OReilly Neonatal Thrombocytopenia 578 47 Chaitanya Chavda, Matthew Saxonhouse, and Martha Sola-Visner Infectious Diseases Viral Infections 588 48 Sandra K. Cloherty 53 Lyme Disease 683 Muhammad Aslam Neurologic Disorders 54 Intracranial Hemorrhage 686 Janet S. Douma Auditory and Ophthalmologic Disorders 64 Retinopathy of Prematurity 840 Deborah K. Stewart and Aimee Knorr Common Neonatal Procedures Common Neonatal Procedures 851 66 Steven A. Douma and Jennifer Schonen Gardner Appendix B: Effects of Maternal Drugs on the Fetus 932 Stephanie Dukhovny Appendix C: Maternal Medications and Breastfeeding 973 Karen M. When premature delivery is inevitable, gestational age is important with regard to prognosis, the management of labor and delivery, and the initial neonatal treatment plan. The clinical estimate of gestational age is usually made on the basis of the rst day of the last menstrual period. Accompanied by physical examination, auscultation of fetal heart sounds and maternal perception of fetal movement can also be helpful. During the rst trimester, fetal crownrump length can be an accurate predictor of gestational age. Crown-rump length estimation of gestational age is expected to be within 7 days of the true gestational age. Strict criteria for measuring the cross-sectional images through the fetal head ensure accuracy. For measurements made at 14 to 20 weeks of gestation, the variation is up to 11 days; at 20 to 28 weeks, the variation is up to 14 days; and at 29 to 40 weeks, the variation can be up to 21 days. The genetic or developmental basis for many disorders is emerging, along with increased test accuracy. Screening tests, such as a sample of the mothers blood or an ultrasound, are noninvasive but relatively nonspecic.
Know that diffuse enlargement of the thyroid is most commonly due to chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis b impotence ginseng buy malegra fxt plus 160 mg visa. Be aware of causes of diffuse thyroid enlargement other than chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis d erectile dysfunction frequency malegra fxt plus 160mg with visa. Know that Hodgkin disease and other infiltrative hematologic diseases (eg men's health erectile dysfunction pills buy malegra fxt plus from india, histiocytosis) and their treatment may involve the thyroid gland 2 erectile dysfunction pump demonstration buy malegra fxt plus 160mg on line. Be familiar with the clinical methods for diagnosis of diffuse enlargement of the thyroid b young and have erectile dysfunction purchase malegra fxt plus 160mg line. Be familiar with the laboratory tests used to evaluate diffuse enlargement of the thyroid c erectile dysfunction causes lower back pain malegra fxt plus 160mg on line. Understand effects of maternal glucocorticoids cortisol on fetal adrenal function 4. Know the normal histology and zonality of the adrenal cortex in the fetus, newborn, and child 5. Know the maturational pattern of synthesis and secretion of adrenal cortical hormones in the fetus, neonate, and throughout early life b. Know the enzymatic steps and genes encoding the enzymes in the pathway of cortisol synthesis from cholesterol c. Recognize the clinical implications of diurnal variations in cortisol secretion 6. Know the conditions in which transcortin cortisol-binding globulin concentrations are increased or decreased 3. Know that most synthetic steroids have low relative binding to cortisol-binding globulin compared to cortisol 5. Understand the role of cortisol-binding globulin and albumin in the transport of cortisol. Know that adrenal steroids passively enter the nucleus to bind with nuclear receptors 2. Understand the effects of glucocorticoids on bone and mineral metabolism and connective tissue 7. Understand that cortisol may activate both the glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors 8. Know that 11-beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 enzyme efficiently inactivates cortisol to cortisone, which prevents hypertension caused by cortisols binding to the mineralocorticoid receptor in the kidneys 9. Understand that steroid hormone receptors are part of a superfamily of nuclear receptors that share homologies and mechanisms of action 2. Understand the recovery of H-P-adrenal axis after chronic suppression with exogenous glucocorticoids b. Understand the hypothalamic pituitary abnormalities that can cause secondary adrenocortical insufficiency f. Know the association of hypoadrenalism with adrenoleukodystrophy and related disorders g. Know that congenital adrenal hypoplasia may be part of an x-linked contiguous gene deletion associated with glycerol kinase deficiency, retardation, and muscular dystrophy j. Understand that adrenal cortical insufficiency may result from congenital adrenal hypoplasia or hyperplasia of various etiologies k. Understand that adrenal hypofunction (cortisol deficiency) may occur after high dose glucocorticoid therapy for as little as 2-3 weeks, and understand symptoms and signs of glucocorticoid withdrawal l. Understand the diagnosis and laboratory evaluation of decreased adrenal cortical function c. Plan replacement therapy for hypoadrenocorticism with glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids as indicated f. Understand that aldosterone secretion can be normal in secondary adrenal deficiency g. Distinguish the key features of late onset and virilizing classic and nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia i. Understand the risk to a patient or relative of a patient of having a child affected with congenital adrenal hyperplasia j. Understand the medical and surgical management of the different forms of congenital adrenal hyperplasia l. Know that adrenoleukodystrophy is an x-linked condition associated with increases of C22-C26 very long chain fatty acids due to a defect in peroxisomal beta oxidation r. Recognize that Addison disease (autoimmune) may occur in association with other non-endocrine disorders s. Know the long-term outcome of the disorders associated with cortisol deficiency v. Know that anti-adrenal antibodies in Addisons are often directed at the 21hydroxylase enzyme x. Know that Cushing syndrome may be produced by systemic or topical (inhaled and dermal) glucocorticoid administration 2. Understand the clinical and laboratory evaluation needed to determine the etiology of hypercortisolism f. Understand effects of glucocorticoid and androgen excess on growth in patients with Cushing syndrome h. Know the disturbance in pattern and significance of serum urine, and salivary concentrations in Cushing syndrome o. Know diagnostic tools available to detect pituitary tumors in Cushing syndrome and the indications p. Know indications and contraindications for removal of pituitary microadenomata in Cushing syndrome r. Know indications for pituitary radiation therapy, either alone or in combination with other therapeutic modalities s. Understand methods of reducing or discontinuing hydrocortisone therapy after surgical treatment of Cushing syndrome u. Understand that radiation therapy is not immediately effective in controlling cortisol secretion, and that other modalities must be used in the interim c. Know that 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity is normally decreased in infancy 2. Know that prematurity is associated with higher levels of Delta 5 steroid hormones than observed in full-term infants 3. Know the maturational pattern of synthesis and secretion of the adrenal gland (androgens) in the fetus, infant, prepubertal and pubertal child b. Understand the importance of aromatase in sex hormone metabolism in the fetus and older individuals c. Understand that the adrenal androgens are largely bound to albumin and to a small extent to sex hormonebinding globulin 2. Understand the relative abundance of various androgens and their biologic sources. Understand that adrenal androgens exert their effect through peripheral conversion to more potent androgens 2. Understand the role of the adrenal androgens at adrenarche in the development of pubic and axillary hair 2. Know that adrenal androgen deficiency or resistance may contribute to paucity of pubic and axillary hair b. Know that androgen replacement can be used to treat adrenal androgen deficiency b. Know that elevated adrenal adrogens can suppress pitutiary secretion of gonadotropins 2. Know the clinical features, differential diagnosis, and laboratory diagnosis of premature adrenarche c. Understand the long-term outcome of classic and nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia in terms of growth and reproductive function. Know the long-term outcome of premature adrenarche in that it may be associated with later ovarian hyperandrogenism and/or insulin resistance f. Know that androgen excess may be found in girls with insulin resistance syndrome b. Understand the therapeutic options for androgen excess of adrenal and ovarian derivation C. Know that the adrenal cortex synthesizes and secretes minimal amounts of estrone and estradiol 2. Know that most adrenal estrogens are derived indirectly from peripheral conversion of adrenal androgens 3. Know the clinical and laboratory findings in patients with feminizing adrenal tumors b. Know the pathways by which cholesterol is transformed to aldosterone; understand how this is different from cortisol synthesis 2. Know the enzymes and the genes encoding these enzymes necessary for the synthesis of aldosterone from cholesterol c. Understand the factors that regulate aldosterone secretion, including the reninangiotensin system 2. Know that vasopressin has a transient stimulatory effect on aldosterone secretion d. Understand that aldosterone circulates in either a non-protein bound form or bound to cortisol-binding globulin or albumin. Know that the renin-angiotensin aldosterone system regulates sodium and potassium homeostasis 4. Understand the role of 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in controlling corticosteroid action on aldosterone-responsive tissues 5. Understand that aldosterone passively crosses cell membranes to bind with receptors 6. Understand that aldosterone promotes active sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion in its major target tissues 2. Know the various causes of salt-losing syndromes and how to differentiate among them d. Know that salt wasting crisis may be due to aldosterone resistance (mineralocorticoid receptor defect) rather than aldosterone deficiency. Know the molecular basis of pseudohypoaldosteronism and related salt losing syndromes 2. Know how to differentiate mineralocorticoid deficiency from mineralocorticoid unresponsiveness b. Understand the clinical presentations of pseudohypoaldosteronism and the variability in aldosterone resistance of different target tissues c. Know that secondary aldosteronism results from angiotensin stimulation of the zona glomerulosa b. Understand the pathophysiology of hypertension due to excess mineralocorticoid secretion or action 2. Know that renin production is characteristically suppressed in hyperaldosteronism b. Know the clinical presentation of patients with excess mineralocorticoid secretion or action f. Understand the medical treatment of hyperaldosteronism due to bilateral adrenal hyperplasia g. Know the treatment of dexamethasone suppressible (glucocorticoid remediable) hyperaldosteronism h. Know the prognosis of hyperaldosteronism due to unilateral aldosteronoma, bilateral adrenal hyperplasia, and glucocorticoid remediable aldosteronism c. Know that licorice ingestion can cause hypertension by inhibiting 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase enzymatic activity 2. Understand that familial early onset, severe hypertension deserves a thorough evaluation for endocrine disorders E. Know that glucocorticoids are important for the development and function of the adrenal medulla b. Understand the measurement of circulating catecholamines and their urinary metabolites 3. Know the different forms of the adrenergic receptor system and their mechanism of function 3. Understand that physiologic catecholamine effects are rapid in onset and quickly terminated 5. Understand the interrelationship between catecholamines and other hormones such as insulin, glucagon, renin, parathyroid, calcitonin, thyroxine, cortisol, and aldosterone 2. Know the syndromes and genetic disorders underlying excessive production of catecholamines and catecholamine metabolites 2. Know the clinical presentation of disorders associated with excessive production of catecholamines b. Know the outcome of treatment of lesions associated with excessive production of catecholamines c. Know the treatment of disorders associated with excessive production of catecholamines d. Know the diagnostic evaluation of disorders associated with excessive production of catecholamines c. Know maturational patterns of individual hypothalamic/pituitary-target gland axes in the fetus b. Know the general structure of pituitary and hypothalamic hormones including which are short peptides, which are proteins, and which are glycoproteins c. Understand the processing involved in transport to , storage of, and secretion of pituitary hormones from secretory vesicles 3. Understand the clinical and physiologic importance of pulsatile secretion of pituitary hormones c. Know the effects of insulin-induced hypoglycemia on anterior pituitary hormone secretion. Understand the function of the hypothalamic-pituitary portal circulation in the regulation of pituitary hormones B.
Malegra fxt plus 160 mg low price. ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION TREATMENT (लिंग ढीलापन की समस्या).
References
- Giunchi F, Fiorentino M, Vagnoni V, et al: Renal oncocytosis: a clinicopathological and cytogenetic study of 42 tumours occurring in 11 patients, Pathology 48(1):41n46, 2016.
- Revencu N, Boon LM, Mulliken JB, et al. Parkes Weber syndrome, vein of Galen aneurysmal malformation, and other fastflow vascular anomalies are caused by RASA1 mutations. Hum Mutat 2008;29:959-65.
- Speeg JS, Vanlangendonck RM Jr, Fusilier H, et al: An unusual presentation of a sciatic hernia. Am Surg 75:1139, 2009.
- Nesser HJ, Mor-Avi V, Gorissen W, et al: Quantification of left ventricular volumes using three-dimensional echocardiographic speckle tracking: Comparison with MRI, Eur Heart J 30:1565-1573, 2009.