Ellen Knox MD MRCOG
- Subspeciality Trainee in Maternal and Fetal Medicine,
- Birmingham Women? Hospital, Birmingham, UK
Staphylococcus avoidance of tap water for cleaning and every 30 minutes for 18 hours 7 Answer key: 1(a) birth control pills until menopause discount 0.18mg alesse with mastercard, 2(d) birth control vaginal ring purchase 0.18 mg alesse visa, 3(e) birth control for women 00 buy alesse once a day, 4(a) birth control without estrogen cheap alesse 0.18 mg with amex, 5(a) birth control for women medical buy discount alesse 0.18mg on-line, soaking lenses birth control pills cramps buy alesse 0.18mg on line. The most appropriate follow-up for Lead Questions for this patient is: References Evaluating Knowledge and a. Microbial hours and cyclopentolate 1% to remove fuid keratitis and vision loss with con(Cyclogyl) bid c. Association between drop every hour and cyclopencultures of contact lens and corneal a. Fusarium scraping in contact lens-related miOptometric Education 51 Volume 37, Number 1 / Fall 2011 crobial keratitis. Review of third and for an increased risk of microbial fourth generation fuoroquinokeratitisfi Fourth generation fuorovarying severity among contact quinolones and bacterial keratitis. Duggiral A, Joseph J, Sharma S, Contact lens-associated microNutheti R, Garg P, Das T. Corneal infltrative penetration into aqueous humor complications associated with in humans. It occurs when the fluid in the anterior chamber reaches the angle between the cornea and iris, and passes too slowly through the meshwork drain. As the fluid builds up, the pressure inside the eye rises to a level that may damage the optic nerve. Glaucoma can also develop without increased eye pressure (called low-tension or normaltension glaucoma). Causes include poor blood supply to the optic nerve fibres, a weakness in the optic nerve structure or a problem with the optic nerve fibres. The lens is made of mostly water and protein, arranged in a way that keeps the lens clear and allows light to pass through. As we age, some of the protein may clump together and start to cloud a small area of the lens, resulting in a cataract that reduces the amount of light reaching the retina. Over time, the cataract may slowly grow larger and cloud more of the lens, making vision gradually duller or more blurred. Hence, although lifestyle changes may reduce the rate of development for some people, cataracts cannot be prevented. New blood vessels grow beneath the retina to supply more nutrients and oxygen to the retina. However, often these blood vessels are in areas where they are not supposed to be; for example, in the macula. Bleeding, leaking and scarring from these blood vessels affect the photoreceptors and impair vision. Poor glucose control during diabetes affects the tiny blood vessels of the retina. The arteries become weakened and leak blood, leading to swelling or oedema in the retina and decreased vision. As diabetes progresses, circulation problems can also deprive the retina of oxygen. New, fragile, vessels develop; however, these are susceptible to bleeding and the blood may leak into the retina and vitreous, causing spots or floaters, along with decreased vision. If abnormal blood vessel growth continues, scar tissue formation may cause retinal detachment and glaucoma may also develop. The condition is diagnosed by using electroretinography to document progressive loss in photoreceptor function. Although the cause of pterygia is unknown, people who work outdoors and are excessively exposed to sunlight and wind more frequently develop pterygia than people who work indoors. Pterygia present as a painless, raised area of white tissues, with blood vessels on the inner or outer edge of the cornea. No treatment is usually required unless the pterygia begins to obstruct vision, and surgical removal of the pterygium usually has good results. Investors may obtain free copies of these documents from Avedro or Glaukos as indicated above. To describe the ocular signs and symptoms associated with selected systemic diseases and their serious ocular sequelae. To review the important features of diabetic retinopathy and the current screening guidelines 3. To be familiar with the important ocular features of hypertension, thyroid disease, sarcoidosis and inflammatory conditions, malignancy and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ophthalmology OnfiCall Survival Guide Updated June 2020, David Ramirez Introduction Starting call as a firstfiyear resident can be challenging, no doubt about it. As you prepare to take primary call, here are some important points to keep in mind: 1. Extensive workups for zebra diagnoses can usually wait until morning, when a wellfirested day team can help evaluate the patient. There will be days when you have hours of free time, and others when 4 true emergencies show up at once. When you are not seeing patients or fielding phone calls, prioritize food, sleep, hydration, and showering. They are your allies in the trenches, and the ones most likely to know where a certain instrument is stored, what a specific attending expects, and to cover your shift when emergencies come up. As you will soon see, our department has a profound and farfireaching legacy of groundfi breaking research, unmatched resident education, and outstanding patient care. Symptomotology Symptom Possible Cause Itching Allergic conjunctivitis Scratchy Sensation Dry eyes, foreign body in the eye, blepharitis Burning Lid, conjunctival or corneal disorders Localized lump or tenderness Hordeolum, chalazion Ocular Pain Iritis, keratopathy, glaucoma, scleritis, infection, orbital cellulitis, corneal abrasions, myositis, Photophobia Iritis, keratopathy, glaucoma, corneal abrasions Mucoid discharge Allergic conjunctivitis, chlamydial infection Watery discharge Viral conjunctivitis, chemical irritants Purulent discharge Bacterial conjunctivitis, corneal ulcer, orbital cellulitis c. If you are coming for an afterfihours or weekend appointment, please enter through the main entrance of the building until you reach a set of locked glass doors. Obtain a callback number (especially if they do not arrive at your agreedfiupon time) D. Triage; determine whether the patient needs to be seen tonight or if they can be seen in clinic. Enter a clinic note just as you would in general clinic using the ophthalmology exam and clinic note template. Page the radiology resident onficall to ensure the proper protocol is being ordered 2. Ask if the patient can be dilated, particularly if Neurosurgery is requesting the consult B. Check all devices in the call bag before you leave and exchange what is needed. Trauma/plastics: Desmarres retractors, utility scissors, paufiques, Westcott scissors, 5fi 0 fast gut sutures (yellow package), 5fi0, 6fi0, and 7fi0 vicryl sutures (purple), lido w/epi 2. Link all consult notes with consult orders (many providers forget to put this in; remind them) 2. All inpatient consults must be staffed by the Ophtho faculty on call within 24 hours a. If the patient looks surgical and other services are mobilizing, let the senior know V. You may be paged about Saturday morning postfiops arriving at the door; generally the fellows know they are there and you do not need to come in for this (you can text the fellows if unsure) 2. Staffing Officially, all inpatient consults are supposed to be staffed by a fellow or attending within 24 hours. It is permissible for the first year resident to contact a fellow directly regarding the staffing of complicated patients if the first year resident has become proficient in the examination of that particular type of patient. On some services, it is standard practice to efimail the fellow (such as the case of an uncomplicated orbital fracture) in order to ask them about staffing. In these cases, it is often unnecessary for these patients to be staffed and also unfair for the patient to be billed for these consults. If the patient needs to be scheduled within 24fi48 hours, call scheduling or efimail them at ophthalmologyschedulers@healthcare. If the patient can be reasonably evaluated prior to the start of clinic ~8:30am, see it to help your colleagues. No need to worry as long as symptoms fit what you expect with the dynamics of a floating bubble. Tearing and pain after the injection is usually due to the toxicity of the iodine and numbing medication. This can also happen if the front of your eye gets scratched (corneal abrasion) during the injection. This usually improves very quickly over the course of 12fi24 hours with rest, Tylenol and artificial tears. If this does not improve (in 12fi24h) or gets worse in any way, call back so we can see you. If the eye is still uncomfortable or if the lens was placed for a corneal wound leak, we can arrange for you to be seen tomorrow to replace it or you can see a local eye care provider if you live a long distance away. Otherwise, tape the protruding end to your cheek and we will arrange to see you tomorrow to replace it. If you can count the number of new floaters on 1 hand, we can arrange to see you in the morning. If there are more floaters than you can count, if you are having associated flashes, if there is a curtain over your vision, or if you have change in your vision, we should see you tonight. Bent Needle: Under low to medium magnification, stabilize your hand and hold the needle parallel to corneal surface as bevel faces the practitioner. Rust ring: Complete removal of a rust ring is not necessary and doing so may damage additional tissue. Post procedure Care: fi Antibiotic (fluoroquinolone qid to 6x/day) fi +/fi cycloplegia fi No patching fi Followfiup in 1fi2 days (most epithelial defects heal in 24fi48 hours) Management: Topical anesthetic will make life easy for everybody. Informed the patient that abrasions can be extremely painful until healed, but they typically heal quickly over the course of 2fi3 days. Exam: fi Check corneal sensation (decreased sensation can suggest herpetic keratitis). Abx gradually tapered as ulcer improves per cornea service (vs if no improvement reficulture vs confocal etc) If patient has a positive fungal corneal culture: *It is common to get call from microfilab over the weekend re: culture results 1. Most likely bacterial*** etiology given risk factors (***contact lens wearer, ***history of recent trauma, ***swimming pool/hot tub use). We discussed the importance of regular follow up and adherence to antibiotic therapy. Tape a label onto each agar plate, tube, and glass slide folder, and one on the specimen bag Procedure webeye. If Concerned about Acanthamoeba *should have senior or fellow present fi Confocal prior to culture (unlikely to be done onficall) Acanthamoeba testing Corneal scrapings need to be sent to both of the following: 1. Anesthesia: Topical Complications: the patient did not experience any complications.
The clinical application of this high-end imaging device will surely expand when its practicability is improved up to a level that a trained technician is able to acquire high quality scans of the same location over time birth control and womens health buy 0.18mg alesse with mastercard. To attain these essential improvements birth control 24 active pills cheap alesse 0.18mg with mastercard, eforts should be made to lower the image acquisition time and to develop an eye-tracking system birth control pills bleeding proven alesse 0.18mg. It is through such invaluable knowledge of cellular morphology in unfxed tissue and the inexorable technological advances that a revolutionary ophthalmic discipline will evolve in the coming years: histopathology of the living eye birth control pills 4 months purchase alesse discount. In vivo confocal microscopy will undoubtedly provide the basis for this new exciting discipline birth control pills 3 weeks order alesse on line amex. Herpes keratitis in the absence of anterograde transport of virus from sensory ganglia to the cornea birth control 9 alesse 0.18 mg for sale. Design and validation of a tool for neurite tracing and analysis in fuorescence microscopy images. Comparison of corneal endothelial cell images from a noncontact specular microscope and a scanning confocal microscope. Objective measurements of corneal light-backscatter during corneal swelling, by optical coherence tomography. Correlation of histology and linear and nonlinear microscopy of the living human cornea. Recent advances in ophthalmic anterior segment imaging: a new era for ophthalmic diagnosisfi Micrometer-scale resolution imaging of the anterior eye in vivo with optical coherence tomography. Clinical and research applications of anterior segment optical coherence tomography a review. In vivo anterior segment imaging in the rat eye with high speed white light full-feld optical coherence tomography. Ocular tissue imaging using ultrahigh-resolution, full-feld optical coherence tomography. Live tissue intrinsic emission microscopy using multiphoton-excited native fuorescence and second harmonic generation. Intraocular multiphoton microscopy with subcellular spatial resolution by infrared femtosecond lasers. Intravital two-photon microscopy of immune cell dynamics in corneal lymphatic vessels. Evaluating corneal collagen organization using highresolution nonlinear optical macroscopy. Three-dimensional analysis of collagen lamellae in the anterior stroma of the human cornea visualized by second harmonic generation imaging microscopy. Quantitative characterization of biological liquids for third-harmonic generation microscopy. Molecular third-harmonic-generation microscopy through resonance enhancement with absorbing dye. Analysis of corneal stroma organization with wavefront optimized nonlinear microscopy. Diagnosis of bacterial contact lens related keratithis with the white-light confocal microscope. In vivo confocal microscopy: a new possibility to confrm the diagnosis of Borrelia keratitisfi An electron microscopic study of basal melanocytes and high level clear cells (Langerhans cell) in vitiligo. Langerin, a novel C-type lectin specifc to Langerhans cells, is an endocytic receptor that induces the formation of Birbeck granules. Infammation and the nervous system: the connection in the cornea in patients with infectious keratitis. The technological advances that preceded the invention of the confocal microscope are described and its main principle of a common focal point of the illumination and observation pathways is discussed. In the last two decades the use of confocal microscopy has clearly made the transition from basic research into ophthalmic practice. We performed three basic studies to enable morphologic cellular assessment to be combined with corneal backscatter analysis, before this powerful combination was studied in herpetic keratitis. This normative study population was evenly distributed over 5 age categories ranging from 20 to 79 years and comprised 75 women and 75 men. Based on this study population, chapter 2 describes the morphologic diversity of the normal cornea and discusses the changes that appear with aging. Because the morphologic diversity of the cornea is enhanced with aging, we conclude that knowledge of the common morphologic variants and of the efects of aging is essential to detect degenerative disorders or pathologic processes in the cornea. Because this turbidity standard is impractical for daily use and garanteed for only 1 year, we proposed a solid reference standard made of polymethylmethacrylate to enable long-term calibration of corneal backscatter measurement. This fnding indicates the necessity to calibrate corneal backscatter measurement in order to compare study results across laboratories. In addition, we determined the interand intrasession repeatability for each of these backscatter variants based on the same normative study population that indicated the morphologic corneal diversity in Chapter 2. The infuence of sex, age, and time of measurement, however, was smaller than the variability between and within subjects. Therefore, we accounted for these efects in a generalized normal range and minimum detectable change for each backscatter variant. Pseudoguttae were the most common alteration, followed by enlarged intercellular gaps, spot-like holes, loss of defned cell boundaries, endothelial denudation, and infltration of infammatory cells into the endothelial layer. These alterations often preceded formation of keratic precipitates and disappeared with appropriate antiviral and anti-infammatory treatment. Despite a 14-year history of presumed herpetic keratitis, a herpes virus origin for the bullous keratopathy could not be confrmed after meticulous analysis of two aqueous humor samples and the excised corneal button. Using immunohistochemical analysis, we did fnd evidence for epithelial metaplasia of the endothelial cells, whereas the zipper-like appearance was characterized by overlapping cells with broad-based extentions at electron microscopy. The in vivo and ex vivo fndings in zipper cell endotheliopathy do not ft any known corneal disorder, but may represent an aberrant wound-healing response to endothelial damage of undetermined source. Also, morphologic assessment of the corneal cells layers may be substituted or enhanced by two-photon excitated fuorescence imaging combined with secondand third-harmonic generation imaging. However, before these non-linear microscopic techniques can be used for in vivo imaging of the human cornea several important restrictions have to be eliminated. In dit hoofdstuk komen de technologische ontwikkelingen aan de orde die voorafgingen aan de uitvinding van de confocale microscoop. Ook wordt het belangrijkste principe van confocale microscopie besproken: een gemeenschappelijk brandpunt van de belichtingsen de observatiearm. In de laatste twee decennia heeft er een duidelijke vertaalslag plaatsgevonden van basaal wetenschappelijk onderzoek naar de oogheelkundige praktijk. Wij hebben drie basisstudies verricht om het beoordelen van de celmorfologie the kunnen combineren met het meten van corneale backscatter. Daarna hebben wet we deze unieke combinatie bestudeerd in patienten met herpetische keratitis. Deze normatieve studiepopulatie bestond uit 75 vrouwen en 75 mannen in de leeftijd van 20 tot en met 79 jaar, gelijkmatig verdeeld over 5 leeftijdscategorieen. Op basis van deze studiepopulatie wordt in Hoofdstuk 2 de morfologische diversiteit van de normale cornea beschreven en komen de veranderingen die optreden door veroudering aan de orde. Wij vonden dat microdeposities in het anterieure stroma, plooien in het posterieure stroma, vertroebeling van het membraan van Descemet en corneale guttata signifcant toenamen met de leeftijd. Doordat de morfologische diversiteit van de cornea verder toeneemt met de leeftijd concluderen wij dat kennis van de veelvoorkomende morfologische varianten en van de verouderingsprocessen essentieel is om degeneratieve of pathologische processen in de cornea the kunnen detecteren. Omdat deze turbiditeitsstandaard niet praktisch is in het dagelijks gebruik en slechts voor een jaar gegarandeerd wordt, stellen wij voor om een vaste stof als referentiestandaard the gebruiken. Deze referentiestandaard bestaat uit polymethylmethacrylaat en maakt kalibratie van corneale backscatter over een langere periode mogelijk. Deze bevinding benadrukt de noodzaak om corneale backscatter metingen the kalibreren. Alleen zo kunnen de resultaten van verschillende apparaten en studies met elkaar vergeleken worden. Daarnaast hebben we voor elk van deze varianten de interen intrasessie herhaalbaarheid bepaald met behulp van dezelfde normatieve studiepopulatie die in Hoofdstuk 2 gebruikt werd om de morfologische diversiteit van de cornea aan the tonen. We vonden dat corneale backscatter 3,5% hoger was in mannen, signifcant toenam in het anterieure stroma na het 50e levensjaar en een beperkte, maar signifcante dagschommeling vertoonde. De invloed van geslacht, leeftijd en tijdstip van de meting was echter kleiner dan de variabiliteit tussen en binnen proefpersonen. Hier hebben wij rekening mee gehouden bij het opstellen van algemeen toepasbare normaalwaardes en minimum detecteerbare veranderingen voor elke backscatter variant. Pseudoguttata waren de meest voorkomende verandering, gevolgd door vergroting van de intercellulaire ruimtes, ronde gaten in het endotheel, vervaging van de celgrenzen, endotheliale denudatie en infltratie van ontstekingscellen in de endotheliale cellaag. Deze veranderingen gingen vaak vooraf aan de vorming van endotheelbeslag en verdwenen schijnbaar volledig met het instellen van adequate antivirale en anti-infammatoire therapie. Ondanks dat zij al 14 jaar bekend was met een veronderstelde herpetische keratitis, kon dit niet bevestigd worden na uitgebreide analyse van twee monsters uit voorste oogkamer en de geexcideerde corneale button. Met behulp van immunohistochemische analyse vonden we wel aanwijzingen voor epitheliale metaplasie van de endotheel cellen. De meanderende vorm van de celgrenzen werd gekenmerkt door overlappende cellen met brede uitlopers bij elektronenmicroscopie. De in vivo en ex vivo bevindingen van Zipper cell endotheliopathy passen bij geen enkele tot nu toe bekende corneale aandoening. Mogelijk vertegenwoordigen ze een aberrante wondhelingsreactie na endotheliale schade van onbekende origine. Ook de morfologische beoordeling van corneale celpopulaties wordt mogelijk vervangen of verbeterd door twee-fotonen excitatie en fuorescentie beeldvorming gecombineerd met tweede en derde harmonische generatie afbeeldingstechnieken. Voordat deze non-lineaire microscopische technieken gebruikt kunnen worden voor in vivo beeldvorming van de menselijke cornea zullen er Samenvatting 187 nog enkele essentiele beperkingen overwonnen moeten worden. Dankwoord Dankwoord 189 dAnkwoord Het is alweer zes jaar geleden dat ik bij Lies Remeijer op sollicitatiegesprek mocht komen. Deze kans was een prachtige opstap om in opleiding tot oogarts the komen en ik wilde dan ook, in mijn onwetendheid, niet langer dan een jaar in het onderzoek blijven hangen. Na vier dagen inwerken door mijn voorgangster Christien Weenen, begon mijn proefperiode van drie maanden waarin vooral een introductie in de wereld van de corneaspecialist en het inventariseren van de mogelijkheden van confocale microscopie op de voorgrond stonden. Met haar uitzonderlijke talent om mensen the doorgronden, had ze natuurlijk mijn ambivalente houding ten opzichte van het onderzoek opgemerkt. Ik was het met haar eens, maar door de verzamelde gegevens was ik inmiddels danig in verwarring gebracht. De gegevens bleken zoveel potentie the hebben dat we ze wel samen moesten uitwerken. Het resultaat is gebundeld in dit proefschrift, maar zal nog jaren doorwerken in vele ideeen voor nieuwe onderzoekslijnen die nog uitgewerkt kunnen worden. Lies, ik kan je niet genoeg bedanken voor al je opoferingen tijdens deze fantastische periode in mijn leven. Je hebt me gemotiveerd, geinspireerd, je bent een voorbeeld in vele facetten van het leven, maar je hebt me bovenal de kans gegeven om mijn droom, om topsporter the worden, waar the maken. Een topsporter kan niet presteren zonder de enorme organisatie achter hem, waarin ieder radertje onmisbaar is. Allereerst wil ik alle vrijwilligers en alle patienten die aan onze onderzoeken hebben meegewerkt, ontzettend bedanken voor hun motivatie om, vaak meerdere malen en soms jaren achtereen, achter de Confoscan plaats the nemen. Een artikel wordt alleen beter door de vakmensen die ieder woord onder een vergrootglas leggen. Beste Jan, dank voor het vertrouwen om de opleiding the mogen combineren met de laatste fase van het promo190 Dankwoord tieonderzoek. Natuurlijk wil ik ook alle co-auteurs, waaronder enkele in het bijzonder, bedanken voor hun waardevolle inbreng. Telkens na de onderlinge gesprekken kraakten mijn hersenen van de vele ideeen die zich ondertussen hadden gevormd. Daarnaast zijn meerdere artikelen naar een hoger niveau getrokken door jouw inbreng. Ik vind het ontzettend leuk en voel me vereerd dat je in de promotiecommissie plaats wilt nemen. Beste Neeltje Mooy, hartelijk dank voor de mogelijkheid om de in vivo corneale morfologie the kunnen staven aan ex vivo histopathologie. Door deze unieke aanpak hebben we Ophthalmology zover gekregen dat ze een case-report hebben geaccepteerd. Arni Sicam, without you I was still struggeling with the standardization of the backscatter measurements. Roger Cals, als oudste co-assistent werd je aan mij gekoppeld om een deel van de onderzoeksgegevens the verwerken. Hoeveel geluk hebben Lies en ik gehad met jouw kennis van programmeren, opgedaan bij de studie werktuigbouwkunde op de T.
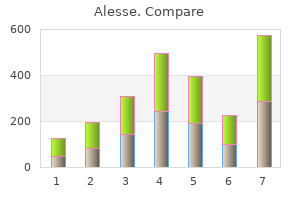
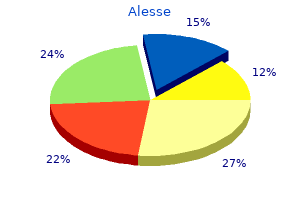
Buy 0.18 mg alesse with amex. MALE BIRTH CONTROL| NEWS STORIES| FROM SINN'S PERSPECTIVE.
Whitthe retina birth control pills canada order 0.18mg alesse overnight delivery, corresponding to those related to the nerves ish fecks surround the ovoid zone of atrophy birth control pills 50 mcg estrogen discount alesse 0.18mg otc, when differof the lids and orbit (see Chapter 32 birth control and periods order alesse in united states online, Ocular Manifestations ential diagnosis from fundus favimaculatus birth control 3 month pack cheap alesse 0.18mg otc, which is often of Systemic Disorders) birth control pills ratings generic alesse 0.18 mg with visa. In the fnal stages the posterior pole shows an extensive chorioretinal atrophy with poor vision birth control pills pregnancy 0.18 mg alesse free shipping. There duce bilateral and usually symmetrical lesions in the abis no leakage of dye. The fundus picture in pearance of the visual elements and the pigment epithelium individuals of the same family is often similar and examinain the centre of the retina. Dominant Foveal Dystrophy this is a progressive tapetoretinal dystrophy of the central retina. Inverse Retinitis Pigmentosa Bone corpuscles are visible in the perifoveal area while the retinal periphery is normal. Histological studies show a progressive degeneration of the neuroepithelium and pigment epithelium. The condidition characterized by a bilateral progressive loss of visual tion is due to an autosomal recessive gene. It is due to a Butterfy-Shaped Pigment Dystrophy primary dystrophy of the retinal cones. Vitelliform Dystrophy of the Fovea Fundus Flavimaculatus Vitelliform dystrophy of the fovea is known as Best disease. White or yellowish-white deep retinal fecks good and the neuroepithelium is unaffected. Serious loss of resembling fsh tails with fuzzy outlines as seen with the vision occurs only after transition to an irregular pigmented ophthalmoscope are characteristic. The central vision the vitelliform disc is probably situated in the pigment falls when the macula is affected. It Reticular Dystrophy of the Retinal Pigment is now considered to be part of Stargardt disease. Epithelium this condition is characterized by a peculiar defned Grouped Pigmentation of the Foveal Area network built up of black pigmented lines consisting of closely packed pigment granules at the posterior pole. Round pigmenfovea itself displays a black spot of about one disc diameter tary spots are present in the foveal area. Visual acuity is Chapter | 20 Diseases of the Retina 339 normal or slightly diminished. They are due to an enzymatic defect in the pigamaurosis in which blindness occurred in early infancy. Initially tiny, round, white fecks appear the essential features are bilateral blindness, with coarse in the posterior pole of the eye. White colloid bodies on the nystagmus and some retention of the pupillary refexes and nasal side of the optic disc may be regarded as pathognothe eventual appearance of pigmentary degenerative monic of this affection. It is a relatively common cause of the ages of 20 and 40 years and is initially without sympblindness in infants. The colloid bodies increase and coalesce and eventuand may remain so in the frst few months of life. In advanced stages a various polymorphic lesions appear, the most typical of central scotoma is found. Dark adaptation, the electrowhich are small white spots in the periphery of the fundus retinogram and the electrooculogram are normal. There are also abnormal areas seen with tually the typical bone corpuscular form of pigmentary fuorescein angiography, indicating a disturbance in the dystrophy develops. In two of them the ganglion cells of the eral infammatory signs in the posterior pole. Inheritance is usually autosomal gradually blind, with muscular wasting and weakness, and dominant. The ophthalmoscopic picture is very characteristic, resembling that of embolism of the central artery. Central Areolar Choroidal Atrophy There is a round, white area at the macula, with a cherryCentral areolar choroidal atrophy is a disease primarily red spot at the fovea (Fig. In the later stages there is affecting the posterior pole in predisposed individuals over optic atrophy, which is always bilateral. A progressive atrophy of the choroidal to an absence or defciency of hexosaminidase A enzyme vessels is found and the choriocapillaris, pigment epithelium leading to storage of ganglioside Gm2 in the central nervous and outer retinal layers gradually disappear. The hetlowish-white area of chorioretinal atrophy evolves and evenerozygote may be detected by decreased enzyme activity in tually central vision is lost. Fluorescein angiography shows intense fuoresdisease): this has an autosomal recessive inheritance, comcence in the area of the visible choroid where the retinal mencing at about 6 or 8 years. Summary the retina is a light sensitive membrane which lines inside of the eye behind the ora serrata. It exists in a double layer with the transparent inner neurosensory retina which converts the light stimulus sensed by its photoreceptors into a signal which can be transmitted along the visual pathway to the brain and the outer pigment epithelium which maintains the photoreceptors and absorbs stray light. Diseases that affect the retina include those that are the result of systemic diseases which affect its vasculature such as hypertensive retinopathy, diabetic retinopathy, retinopathy of prematurity, etc. Online multimedia database endorsed by the International Council of ripheral blood are vacuolated. The vitreous is clear and avascular, flling the Cloquet canal, which contains the primary vitreous space bound by the lens, retina and optic disc, it occupies at birth, runs straight from the lens to the optic disc. The internal secondary vitreous eventually becomes liquefed and limiting membrane, on the inner surface of the retina, sepashrinks. Between 40 and 70 years of age in most individuals rates it from the vitreous and there exists a potential space, and earlier in myopes, vitreous liquefaction or syneresis the subhyaloid space, between the two. Condensations of the (hyalocytes), and mucopolysaccharides, forming a gel-like vitreous fbrils are present within this liquefed vitreous and material. When they foat into the optic axis, undergoing turgescence and deturgescence and readily especially against a bright background, they can be seen as becoming liquefed when its protein base becomes coagumuscae volitantes in various shapes and sizes. The vitreous should appearing spontaneously, producing a sudden onset of be observed for cells and any opacities. As the patient photopsiae (see Chapter 9, Ocular Symptomatology) and moves his eye, any settled opacities rise up into the path foaters. The vitreous in such be projected in the meridian opposite to the site of retinal cases is liquefied and no treatment is indicated. Patients complain of a ring-like opacity, Weiss l Amyloid degeneration: Amyloidosis is a rare systemic ring, which is the detached attachment of the vitreous to the disease and amyloid material is deposited in the coledges of the optic nerve head. The conditransmitted as a Mendelian dominant producing genertion is benign unless it is associated with other pathological alized weakness, loss of weight, peripheral neuropathy fndings, such as retinoschisis, a rhegmatogenous retinal and symptoms related to the affected organs. The clinical features consist Patients with posterior detachment of the vitreous must of diplopia, diminution of vision, external ophthalbe carefully examined, and reassured if there is no evidence moplegia, vitreous opacities, retinal haemorrhages of retinal tear, peripheral retinal degenerations, or vitreoand exudates. The earliest lesion originates in the wall of a retinal vessel which has a cloudy margin and this slowly invades the vitreous body from behind forAnterior and Basal Vitreous Detachments wards. Diagnosis is confirmed by biopsy of the conthese occur secondary to trauma and are often accompajunctiva, rectum, skin or sternal marrow. A commonly mistaken for small fying insects, and are termed senile or myopic eye produces opacities due to condensed muscae volitantes or foaters. They can also be formed by the infammatory cells of cyclitis, haemorrhage secondary 1. Developmental opacities which are located in the canal to diabetes, retinal vasculitis or subarachnoid haemorrhage of Cloquet and are remnants of the hyaloid system, or and occasionally by neoplastic cells. These vitreous detachment and originate from hyalocytes, fbroare calcium-containing lipid complexes attached to cytes, migratory retinal pigment epithelial cells in the presthe collagen fibrils and suspended throughout the ence of a retinal hole, or endothelial cells of the capillaries. If such a band is adherent to the retina and is producing It is unilateral in the majority of cases and affects photopsia, retinal oedema or haemorrhage then the traction both sexes, is asymptomatic but may make examinais likely to give rise to retinal breaks or a detachment. In some diseases, a preretinal or epiretinal membrane Treatment is rarely required unless vision is affected, lines the inner surface of the retina; if it is thin it looks like a in which situation a vitrectomy may be considered. These are also found in the anterior chamber and progress to threaten central vision and cause a signifcant subretinal space. It affects damaged eyes which have visual handicap, as evidenced by metamorphopsia and may been subjected to trauma or inflammatory disease in then be removed by vitrectomy with dissection of the memthe past. They are commoner in older people and are often bicles which settle in the lower part of the vitreous cavity lateral though asymmetrical. Pars plana vitrectomy combined due to gravity but can be thrown up by eye movements with epiretinal membrane stripping is effective, particularly in Chapter | 21 Diseases of the Vitreous 343 treating macular pucker, though the complication of cataract have an extensive tractional retinal detachment for which would seem to be an unavoidable risk. In the posterior fundus they consist of oedema of the retina, Wagner disease is a bilateral condition transmitted as an haemorrhage, macular cystoid changes, heterotopia of the autosomal dominant trait. There is a failure of the structures within the primary vitreous Extensive liquefaction of the central and posterior portions to regress. Shortly after birth a unilateral, white pupillary of the vitreous body takes place leaving a thin layer of refex is noticed in the full-term infant, which may later be formed cortex on the surface of the retina. In the presence of severe vitreous traction, the retrolental tissue contracts over time to pull the vitreoretinal surgery is indicated. Ultrasonography and computed hereditary progressive arthro-ophthalmopathy and is a tomography are helpful in diagnosing this condition. This is an autosomal domiagnosed at an early stage it may be possible to aspirate the nant connective tissue disorder affecting the ears, eyes lens followed by excision of the retrolental membrane and and joints. They may also have a the posterior form of persistent hyperplastic vitreous cleft palate, bifd uvula and sensorineural deafness. Ocular includes a persistent hyaloid artery with a large stalk issuinvolvement includes a progressive myopia, spontaneous ing from the optic disc (Fig. The affiction is bilateral and familial, being transmitted as an autosomal recessive trait. It may be localized to the preretinal space, intravitreally located or, more often, may be present in both. Extensive chorioretinal degeneration and a pigmentary the haemorrhage commonly settles inferiorly, a reasonable retinopathy can also be seen. Blood in a lacuna of the vitreous indicates a reasonable chance of anatomical success. Active tends to separate whereas blood in the gel clots and moves treatment is particularly indicated if the fellow eye is bodily with the gel itself. Vitreous Haemorrhage and Retinal Tears Ultrasonography with a B-scan is particularly helpful. Fresh haemorrhage within the vitreous cavity gives rise to Retinal tears crossing a blood vessel can lead to vitreous scattered point-like echoes of varying amplitude. This tends to occur in myopes and in those who tation of haemorrhage within the fuid vitreous produces a have predisposing degeneration of the retina. Posterior vitreous localized fashes and foaters before the onset of the haemordetachment is indicated by point-like echoes confned to the rhage itself and may be precipitated by mild ocular trauma. Extensive fbrovascular membranes on the retinal surface may be detected by Vitreous Haemorrhage and Posterior ultrasound in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Diabetic Vitreous Detachment traction detachment appears as an angular retinal elevation that is immobile on dynamic testing. Bleeding in association with posterior vitreous detachment the common causes of vitreous haemorrhage are prolifis due to retinal traction and may occur in the vitreous gel, erative diabetic retinopathy (Fig. Trauma is the commonest cause in posterior vitreous detachment usually clears spontanethe young. If a bleeding vessel can be seen it should be photoEarly surgical intervention is required in eyes having a coagulated. Other causes can be managed conservatively with the Vitreous Haemorrhage and Retinal Vein head elevated so as to minimize the dispersion of blood Occlusion within the gel. If the blood sinks under the infuence of gravity it may be possible to discover a cause which should Venous obstruction occurs at the lamina cribrosa or at be treated.

Neonatal death occurs anytime between complete delivery of the infant and the end of 28th day of extrauterine life birth control pills for heavy periods generic 0.18mg alesse free shipping. Significant if there is differential congestion on either side of the knot or an associated mural thrombus and evidence of hemorrhage birth control for women growing order alesse 0.18mg without prescription. Placental Disc Abnormalities Abruptio placentae is related to 15% of fetal deaths birth control pills 50 mcg order genuine alesse. It may be due to abdominal trauma; uterine tumors; hydramnios birth control 999 effective purchase 0.18 mg alesse with amex, short umbilical cord birth control junel fe discount alesse on line, sudden decompression of the uterus; occlusion or compression of the inferior vena cava birth control for women zapatistas discount 0.18 mg alesse, lupus erythematosus; and the use of anticoagulants (Figure 2. Other causes include acute chorioamnionitis, coitus, increased maternal age (more frequent arterial and arteriolar damage), maternal cigarette smoking, and maternal hypertension. Causes and associations include pregnancy-induced hypertension, lupus anticoagulant, and antiphospholipid antibodies. Heavy deposition of fibrin in the decidua basalis occurs and encases villi; 17% of fetuses are stillborn; chorioamnionitis and intrauterine growth retardation are strongly associated. Fetal Abnormalities in Stillbirths Maceration occurs if there is intrauterine fetal retention after fetal death. The extent of maceration in stillborn fetuses may be a rough indicator of the time interval from fetal death to delivery; however, its rate may be infiuenced by maternal fever, fetal or placental infection, fetal hydration at the time of death, amniotic fiuid volume, and delay from delivery to postmortem examination. Maceration may hinder, but does not negate, the pathological investigation of the stillbirth. Placental changes after fetal death appear to be more constant; if cytotrophoblasts are increased without stromal changes, fetal death has occurred in <7 days. Stromal fibrosis, calcifications, syncytial knotting, and thickening of the basement membrane occur >7days after the death of the fetus (Figure 2. Laxity and dislocation of joints Trachea: chondrocyte loss of nuclear basophilia 2 weeks Mummification (dehydration, Extensive vascular luminal change compression, tan color) (see 48-hour findings). External fetal examination: A study of 86 stillborns, Obstet Gynecol 80:593, 1992. If large may cause: fetal death fetal distress hypovolemic shock anemia with cardiac failure hydrops (Figure 2. This test is based on different acid elution characteristics of fetal and adult hemoglobin. The test should be done routinely in all cases of unexplained stillbirth, fetal distress, and neonatal anemia. Immediate transfusion may be lifesaving, and testing of the mother during the puerperium is still important. The size of the hemorrhage can be calculated on the basis of the percentage of fetal red cells present (number of fetal cells in 2,000 total red cells divided by 20), an estimated average maternal blood volume of 5,800 mL, an average maternal hematocrit of 0. For example, if 5% of the red cells in the maternal circulation are fetal in origin, the size of the hemorrhage is calculated as 5,800 fi 0. The infant is at risk for placental insufficiency and perinatal hypoxia, intrauterine distress, respiratory distress syndrome,andstillbirth. Some postdate newborns have no biochemical, physiologic, or other signs of placental dysfunction. Theskiniswrinkled which, after separation breathes or shows any other evidence of life, such as and meconium stained. In the United States, 20% occur in the African-American population and 9% in the white population. The major complications of prematurity are hyaline membrane disease that may progress to bronchopulmonary dysplasia, necrotizing enterocolitis, and germinal matrix and intraventricular hemorrhage. Prematurity is defined as a weight of 2,500 g or less or a gestational age of <37 weeks (Figures 2. The hand and foot show nails extending beyond the tips of the digits and meconium staining of skin and nails. Very-low-birth weight infants weigh 1,500 g or less and constitute 1% to 2% of all live births. Prematurity and complications of preterm birth tissue and low birth weight result Hyaline membrane disease and bronchopulmonary dysplasia Absence of lanugo hair Intracranial hemorrhage Long nails Necrotizing enterocolitis Abundance of scalp hair Diffuse pulmonary hemorrhage Pale skinwith desquamated 2. Maternal complications of pregnancy Dehydration Age Hypoglycemia Parity Complications of placenta/cord/membrane Smoking Hypertension and preeclampsia Postmaturity Diabetes mellitus Thyrotoxicosis Collagen vascular diseases 7. Severe cerebral edema of brain ina cigarette smoking during pregnancy, vigorous motor activity by the fetus, a newborn who sustained severe birth anoxia. Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy is the result of perinatal asphyxia usually occurring at or shortly before birth. The cortex, basal ganglia hippocampus, brain stem, and cerebellar Purkinje cells are primarily affected. Initially the cysts were separate from the ventricles, but communication subsequently developed. It usually is a complication of hypoxia in a premature infant but may occur in full-term infants. Porencephaly Perivascular leukomalacia may progress to porencephaly with coalescence of small cysts to form large cystic spaces that may communicate with the ventricles. Twenty-five hundred cases occur annually in the United States and 20% to 60% require surgical treatment. In stage I, the infant manifests abdominal distension, vomiting, increased gastric residual, lethargy, apnea, bradycardia, or guaiac-positive stools. Surgically manifested by shock, disseminated intravascular coagulation, acidosis, thromresected segment of bowel with hemorrhage bocytopenia, and sometimes intestinal perforation. The bowel is grossly distended, dark purple or black in areas containing extensive hemorrhage; the soft, friable wall may perforate when the involvement is severe and transmural. Perforation occurs at a junction between normal and necrotic bowel or in a devitalized region. In neonates with severe anoxic episodes, blood is diverted to the heart and the brain and the bowel are exposed to severe ischemia. Necrosis of the bowel in some cases may be secondary to mesenteric thromboembolism. Microorganisms isolated from the stools include Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Pseudomonas, Salmonella, Clostridium perfringens, Clostridium difficile, Clostridium butyricum, coaglulase-negative staphylococci, coronavirus, rotavirus, and enteroviruses. Congenital Malformations Congenital malformations are a leading cause of death in neonates. Causes of neonatal deaths from major organ system anomalies include cardiovascular, pulmonary, renal, central nervous system, musculoskeletal, and gastrointestinal malformations as well as chromosomal defects and multiple congenital anomaly syndromes. Bacterial infections may result in neonatal pneumonia, meningitis, or encephalitis. Infant of Diabetic Mother the infant of a diabetic mother is at particular risk for severe hypoglycemia, hyperinsulinemia with pancreatic islet cell hyperplasia, malformations, and Table 2. Complications of Amniocentesis (see Chapter 10) Amniotic Fluid and Meconium Aspiration Amniotic fiuid aspiration is most likely to occur in a hypoxic infant. It usually improves within 48 hours of birth, but if severe it carries high mortality. Meconium aspiration syndrome occurs in 9 per 1,000 births; 59% have been attributed to severe acute chorioamnionitis and less frequently to low uteroplacental blood fiow and abruptio placentae. Occipital diastasis (separation of the squamous and lateral parts of the occipital bone) (Figure 2. At autopsy, refiection of the scalp downward as far as the foramen magnum is necessary to explore fully the occipital bone. The lower Stimulation of uterine contractions edge of the squamous occipital bone is then displaced and rotated forward. Fetal skin puncture with healing to form small scars or dimples Blood Dyscrasia Peritoneal adhesions Ileal atresia 1. Hemolytic disease of the newborn due to blood group incompatibility Fetal intracranial hemorrhage (Figures 2. Protein S, protein C, and antithrombin deficiencies Foramen magnum from above A B C D 2. Metabolic Disorders (see Chapter 24) Metabolic disorders have been related to unexpected death in newborns. In these disorders, there is usually a normal period immediately after birth followed by hypoglycemia, respiratory difficulty, vomiting, and acidosis. Bilirubin staining of basal ganglia (left) and the olivary nuclei (right) inan infant with erythroblastosis fetalis. Bergsjo P: Introducing two international studies on perinatal and infant growth, morbidity and mortality. The variety and complexity of the congenital anomalies found in perinatal and fetal autopsies is endless and the prosector must be prepared to spend the necessary time demonstrating these anomalies. This detailed procedure can be altered to preserve any anomaly encountered without deforming the body itself. Together with the clinical information this meticulous examination provides the necessary information to educate the families about future pregnancies. However, changes occur that resemble vascular insufficiency but are diffuse, affecting fetal structure and all villi (Figure 3. Within weeks, ingrowth of fibroblasts ultimately completely obliterate the vessels. Loss of fetal perfusion leads to stromal fibrosis, loss of capillaries with retention of trophoblasts from maternal perfusion. It presents as fine granules deposited along the basal membrane of the trophoblast, sometimes almost in linear fashion. The fine granules contrast with the coarse deposits that sometimes occur in villi during physiological maturation. The villi are eventually clustered more closely together and the intervillous spaces become almost completely obliterated. When the fetus is severely macerated, amniotic membranes can be used for karyotypic analysis. Mammogram films used in the faxitron with a fetus of 18 weeks gestation positioned to obtain anteroposterior (A) and lateral (B) views. The faxitron is not limited to bony surveys and can be used to demonstrate visceral anomalies through injection studies. By injecting a radiopaque liquid, such as barium or an ionotropic contrast,fistulas can be demonstrated, particularly for bronchial morphology and extrahepatic and intrahepatic biliary ducts without disrupting the anatomy. This is most beneficial in small fetuses (<20 weeks gestation) where the structures are extremely small. The external features may provide the only information necessary to make the diagnosis of a malformation syndrome. The photographs must be close enough to depict the abnormal features with adequate points of reference remaining in the field. Injection study to determine bronchial anatomic relationships and depicting the initial presentation of visceral lesions morphology in a fetus at 14 weeks gestation, with asplenia. In the autopsy a good photograph is often more valuable than phologicright bronchi (arrows). These small instruments are too small for general autopsy purposes and can be destroyed by using them for even one adult autopsy. A good family history is very important, especially any information about other perinatal or neonatal deaths. Illustration demonstrating outer (A) and inner (B) canthal and interpupillary distances 3. The external exam is systematically performed on all fetuses regardless of gestational age (Figures 3. In macerated fetuses, it is present for a considerable length of time in skin creases, such as the axillae, groins, and behind the ears. When meconium is suspected, a cotton swab can be placed in the external auditory canal and/or the nostrils. Cottonswabdemonstratingmeconium vernix caseosa in the groin areas of a macfrom the external auditory canal inastillborn erated, stillborn fetus at 37 weeks gestation. The systematic external examination should be performed with an autopsy protocol in hand. Jaundice can best be assessed in the sclera and cyanosis in the fingernail beds and vermilion border. All catheters and tubes should be left in place until the distal end can be observed or palpated during the internal examination. These can be removed and weighed and then subtracted from the initial weight of the infant to equal the true weight.
References
- Vashchenko N, Abrahamsson PA: Neuroendocrine differentiation in prostate cancer: implications for new treatment modalities, Eur Urol 47(2):147n155, 2005.
- Rajfer J, Handelsman DJ, Swerdloff RS, et al: Hormonal therapy of cryptorchidism. Arandomized, double-blind study comparing human chorionic gonadotropin and gonadotropin-releasing hormone, N Engl J Med 314(8):466n470, 1986.
- Tracey I, Mantyh PW. The cerebral signature for pain perception and its modulation. Neuron. 2007;55(3):377-391.
- Bahls FH, Ozuna J, Ritchie DE. Interactions between calcium channel blockers and the anticonvulsants carbamazepine and phenytoin. Neurology. 1991;41:740-742.