Penina Segall - Gutierrez MD, MSc
- Assistant Director, Fellowship in Family Planning
- Assistant Professor of Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Keck School of Medicine
- University of Southern California
- Los Angeles, California, USA
If unrestricted discharge is not permitted women's health shaving tips sarafem 10mg otc, in some cases a calculation of the actual discharge and dilution may permit a limited number of patients and total activity to be discharged without treatment of the effluent [12 breast cancer yati bahar blogspot generic sarafem 20 mg online. It is quite important that the local regulatory authority is consulted menstrual joy questionnaire cheap sarafem 10 mg with mastercard, and the necessary approvals gained before unrestricted discharge is commenced breast cancer kills order 20 mg sarafem overnight delivery. If a restricted discharge is possible breast cancer 5k columbia sc discount 10mg sarafem with amex, the calculations must be made to the satisfaction of the regulatory authority womens health 28 day fat blaster order sarafem 20 mg on line. Delay and decay Unrestricted discharge is however, not permitted in a number of countries. For example the 131 -1 Canadian limit for discharge of I through the sewer is 370 Bq. To reach the required 8 specific activity limit would require this to be diluted into 7. Hence the waste cannot be simply discharged, and some form of treatment must be used. The only treatment of radioactive sewage practical is to store it temporarily in tanks, for a period long enough for the activity to decay to a level where it may be discharged. Delay tanks can be expensive and complicated, adding significantly to the cost of a radioiodine treatment facility, possibility of increased exposure to maintenance staff and with further possibility of accidental exposures in the event of calamity. From the above, the required decay time can be calculated, and thus the volume of the storage tank. The 156 resultant tank volume is usually in the range 2000 to 4000 litres, with decay periods around 131 4-8 weeks. Owing to the absorption of the I photons in water, there is normally little special shielding required, as long as the tanks are in a controlled access area. There will however, be the need for control and monitoring systems to allow the tanks to be operated and checked remotely, and with appropriate emergency systems. Single decay tanks may be used, but these require a large volume, and longer decay period to allow the permitted average specific activity. In principle, this is a large volume tank with the discharge point at the opposite end from the entry. The assumption is that by the time a particular litre of effluent migrates to the discharge point, it has undergone sufficient decay. Radiotherapy the successful treatment of thyroid cancer depends on the histology of the cancer, its size, presence of metastasis. Overall survival in papillary thyroid cancer 131 significantly improved with and without use of I therapy. On subset analysis, patients of age more than 40 years, and those with T-3 and T-4 disease experienced improved survival which was statistical significance. These cancers slowly regress after radiation therapy often requiring more than a year to obtain the maximum response, analogous to the situation 131 when I is used to treat gross disease. Radiation therapy is particularly useful for treating the thyroid bed when residual microscopic disease is suspected. Under ideal clinical circumstances, however, this will be a rare requirement, as patients should have adequate surgical removal of gross thyroid tissue followed by radioiodine treatment. There is no place for small volume irradiation in the primary treatment of this tumour. However, growing knowledge of the specific genes involved in thyroidal oncogenesis may contribute to the future development of more effective treatment modalities [13. However, local control and cure rate are not synonymous, and despite local control, the majority of patients die of disseminated disease [13. Lymphoma Combined chemotherapy and irradiation are effective in thyroid lymphoma [13. Consequently, total thyroidectomy should no longer be considered the first-line treatment. Other histologic varieties, including Hurtle cell carcinoma are characterized by advanced disease at the time of diagnosis and by may be unresponsive to treatment. Except where there is a clear-cut palliative benefit often, these malignancies go untreated because the acute complications may exceed any benefit produced by surgery, irradiation or chemotherapy. Introduction the role of chemotherapy in differentiated thyroid carcinoma is limited, unlike other solid malignancies where it is widely used as an adjuvant therapy. Most differentiated thyroid carcinomas can be successfully treated by the combination of surgery, radioiodine and L- thyroxine suppressive therapy. The role of chemotherapy is restricted to the treatment of i) locally advanced or metastatic nonfunctioning or non-iodine concentrating differentiated thyroid cancer, ii) anaplastic thyroid cancers, and iii) advanced metastatic medullary thyroid cancers. Chemotherapeutic agents are used either as monotherapy or in combination with more than one drug. In order to increase the effectiveness and decrease the toxicity of drugs, they are also used along with other treatment modalities (multimodal treatment), particularly with external beam radiotherapy. Addition of chemotherapy to surgery and external radiotherapy is reported to improve the survival in medullary thyroid cancer [14. Differentiated thyroid cancer Chemotherapy is rarely used for management of differentiated thyroid cancers and hence the experience is limited. Only relatively few patients have received chemotherapy for locally advanced carcinoma or metastatic disease. The first chemotherapeutic agent to be used to treat differentiated thyroid cancers was bleomycin. Another drug used more widely with some success, probably most effective mono-chemotherapeutic agent used so far, was Doxorubicin. The overall response rate reported in 83 patients of differentiated thyroid cancers from eight studies was 38. Further, Doxorubicin therapy is 2 associated with cardiotoxicity occurring at doses of 550 mg/m and above. Other chemotherapeutic agents used were methyl-chloroethyl-cyclohexyl-nitrosourea, Rubidazone, peptochemiol, Aclarubicin, Mitoxantrone, endoxan and Pepliomycin [14. These drugs were either ineffective or had very limited, non-lasting effects on the tumour suppression. Usually, a patient who responds to the first drug given is likely to respond to a second drug and that patients who do not respond to the first will rarely do so to other drugs. Since a single agent was not effective and associated with side effects, multi-drug therapy 2 using various combination of drugs and dosages have been tested. The results have been disappointing and average response rate of multiple-agent chemotherapy appears to be only slightly better than that of doxorubicin single-agent chemotherapy. Anaplastic cancer In contrast to the indolent differentiated type, anaplastic giant cell thyroid carcinoma is one of the most aggressive tumours in humans. Mean survival without treatment is 3 to 6 months, and single modality treatment does not seem to change the survival time [14. In the management of anaplastic cancer, chemotherapy is more frequently used as these tumours do 131 not concentrate I and are more often unresectable. Doxorubicin monotherapy alone or in combination with external radiotherapy has resulted in a response rate varying between 10-22% [14. Treatment with Bleomycin showed a partial response rate of 25% in primary tumours and 50% in lymph node metastases [14. Aclarubicin was found to be ineffective with a brief partial response of only 14% [14. Methotrexate (5 mg/day, for 5 days) treatment with external radiotherapy (40 Gy in divided doses over 5-6 weeks) in five patients has been reported to result in complete regression of primary tumour. However, patients had severe side effects and they died due to local tumour recurrence and pulmonary metastases within 5-13 months [14. Sixteen patients were treated with pre- and postoperative doxorubicin and hyperfractionated radiotherapy. Of these, five patients had a complete remission, and two patients survived more than 2 years [14. They found the response rate to be significantly better in combined drug therapy as compared to monotherapy. Although, they found complete response in 18%, which lasted for more than 1 year, 73% of cases had a progressive disease indicating the ineffectiveness of the treatment. However, most of their patients developed distant metastases and died (median survival 1 year). A higher success rate (4 with complete response and 5 with partial response in a total of 10 2 evaluable cases) has been reported using multimodal treatment with doxorubicin (60 mg/m) 2 and cisplatin (90 mg/m) along with a split course of external radiotherapy [14. This regimen was effective in longer survival and local control, but was ineffective in controlling distal metastases. They obtained complete local remission in 48% and four patients survived for more than 2 years with no evidence of disease. A total of 16 patients (Group 1) were treated with total thyroidectomy, radiotherapy and chemotherapy with adriamycin and bleomycin in various order. Nine patients with distant metastases at diagnosis (Group 2) received chemotherapy; one of them had a disappearance of lung metastases and was then treated by total thyroidectomy and further chemotherapy. Only a few patients responded to chemotherapy, confirming that anaplastic thyroid carcinoma is often resistant to anticancer drugs. They concluded that aggressive and appropriate combinations of radiotherapy, total thyroidectomy and chemotherapy may provide some benefit in patients with anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. Preoperative chemotherapy and radiotherapy may enhance surgical resectability of the primary tumour. A combination of carboplatin and epirubicin was administered at 4- to 6-week intervals for six courses in fourteen patients with poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma and nonfunctioning diffuse lung metastases. Five patients had partial remission, and seven patients had disease stabilization. The overall rate of positive responses was 37% that rose to 81% when patients with stable disease were included. Serum thyroglobulin after chemotherapy declined more than 50% in six patients, with respect to basal levels. The appropriate treatment strategy of anaplastic thyroid cancer is yet to be evolved. Medullary thyroid cancer Medullary thyroid cancer is a neoplasm of calcitonin secreting parafollicular C-cells of the thyroid gland. Medullary thyroid carcinoma may have an indolent behaviour and patients with distant metastases do well. As this cancer does not accumulate radioiodine, these patients are left with only option of chemotherapy with or without radiotherapy in cases of disseminated disease. Reports on the use of chemotherapy in medullary thyroid cancer are limited to a small number of cases and at times is a single case report. The combination of doxorubicin and cisplatin showed response rate varying between 0-33% [14. Although, there was not a single complete response, there were three partial responses lasting for 9, 10 and 18 months. There was no complete response either in terms of tumour size reduction or decrease in the levels of tumour markers. Two patients had partial biochemical response and reduction in tumour size; one had partial biochemical response with stable tumour size, while three had progressive disease. The response was partial regression of tumours in three patients (at 11, 9 and 3 months) and stabilization of the disease in 11 patients. Yet another 2 2 combination of doxorubicin (45-70 mg/m), imidazole carboxamide (600-800 mg/m), 2 vincristine (2 mg) and cyclophosphamide (600-750 mg/m) has been tried. There was progressive improvement in three patients and one patient had progressive disease [14. Hence although there is no hope of a complete response, it appears that single or combination drug regimes can in a small number of subjects induce a partial response or stabilize disease for some months. There is not enough data to indicate whether the partial response is transient or long lasting. Conclusion the response to chemotherapy in patients with advanced differentiated thyroid carcinoma is not encouraging. Doxorubicin, cisplatin, and etoposide alone or in combination are the drugs currently considered effective. However, side effects may be severe and chemotherapy cannot as yet be routinely recommended. Chemotherapy in combination with external radiotherapy should be tried in cases of anaplastic thyroid cancer and chemotherapy remains the only alternative, though not very effective, in cases of aggressive and widespread medullary thyroid cancer. Chemotherapy in metastatic non-anaplastic thyroid cancer: Experience at the Institut Gustave-Roussy, Tumouri 76 (1990) 480-483. The success of this management structure is highly dependent on the bulk of thyroid tissue left behind after thyroidectomy and the effectiveness of ablation. Its disadvantages include relatively low specificity and sensitivity, its tendency to induce stunning and the need for intensive patient preparation including withdrawal of thyroxine for at least 3-4 weeks and adopting a strict iodine-free diet that may not appeal to all patients. When uptake by residual or recurrent tumour is documented, it can 131 be assumed that the tumour is amenable to treatment with a subsequent therapy dose of I (Fig. However, the issue of stunning has thrown doubt on the effectiveness of an immediate therapy dose following a diagnostic scan.

Time at which recurrences occur in patients who presented with thyroid nodules menopause heart palpitations order sarafem on line amex, nodal and distal metastases women health center buy sarafem cheap online. In this report pregnancy 0-40 weeks order sarafem 10 mg with mastercard, age greater than 60 years women's health clinic somerset ky buy genuine sarafem, extent of tumour breast cancer in men purchase 10 mg sarafem free shipping, tumour size of 4 cm breast cancer youngest age order 20mg sarafem visa, type of surgery and time period of surgery were found to be significant predictors by 181 univariate analysis. In a larger series, in patients who had a potential curative operation at their initial treatment, these authors reported that an age less than 20 years, tumour size greater than 4 cm, presence of nodes and locally invasive disease were significant predictors for nodal recurrence by univariate analysis. The brain was the most common site for secondary and tertiary metastatic recurrences. This was attributed to the rather low mortality observed in patients to the vigorous multimodal treatment offered. The reported probability for survival has been 60-99% at 5 years, 50-97% at 10 years, 35-95% at 20 years and 78-93% at 30 years. Probability of survival of papillary cancers who present with thyroid nodules, nodal or distal metastases. However, as these tumours grow very rapidly, it is likely that they have become less differentiated 131 resulting in reduced capacity for I uptake. In this series, the 5 and 10 year survival rate in 131 metastases concentrating I was 93. As observed by us and reported by others, 131 the metastasis that concentrate I i. The survival for patients in intra-thyroidal and nodal disease is believed to be excellent as evident by overall survival rates of 96-98% and recurrence rate of less than 10% [16. Distant metastases portend poor prognosis regardless of treatment as observed by us and reported by others [16. Shows recurrence rate in follicular cancer when presented with thyroid nodule, nodal and distal metastases. In fact in one study, it has been shown as an independent predictor for adverse outcome [16. The rather high mortality resulting from recurrence of disease indicates that 184 treatment should aim at reducing the recurrence to a low level so that eventually the mortality due to cancer can be reduced and controlled. This has been perhaps because of early diagnosis and availability of sophisticated techniques for management of the disease. An individual with nodal disease is therefore at a high risk for mortality if the (a) nodal disease 131 131 does not concentrate I, (b) disease recurs and (c) I treatment has not been received. Survival rate of follicular cancers when presenting with thyroid nodules, nodal or distal metastases. The 10 and 15 year survival for patients with pulmonary metastasis in this series was 74. The outcome of the disease depends upon the 131 site to recur, with a better outcome for pulmonary metastasis, which concentrate I [16. Similar 131 findings of better survival in metastatic disease concentrating I as compared to those, which do not concentrate, have been observed by others also [16. When matched for age and sex, the mortality in follicular and papillary types of the tumour has been comparable. There was no significant difference in the mortality rate when the intra-thyroidal disease was matched for both types of histology. The lung metastasis had a better prognosis as compared to skeletal metastases as observed by us and reported by others (Table 16. In contrast, some studies have reported comparable results between the two types of tumours when matched for the extent of the disease. Early detection is essential for instituting therapy with Radioiodine when concentration is observed or surgery where possible and external radiotherapy if disease is extensive and surgery is not possible or disease removal is partial. This could be transient or permanent in nature requiring frequent 2+ administration of calcium (Ca) along with calciotropic substances. The calcemic status of the patient following thyroid surgery depends upon the degree and the extent of damage or loss of the parathyroid glands. These patients were followed up from a minimum of 2-3 years, to a maximum of 15-20 years, and calcemic status was ascertained at varying times following their surgery and radioiodine 2+ therapy. The minimum period of ascertaining Ca status varied from 4-6 weeks after surgery, to at times several years later. The over all distribution of these patients in different age groups in both the sex, indicated the predominance of female population (Fig. They were investigated for the circulating levels of Ca before I treatment and further on every follow-up examination and evaluation. In 2+ general the serum Ca should be kept at or below the lower end of normal to prevent hypercalceimia (Fig. Regular monitoring, preferably at 3-6 months intervals is necessary to detect any spontaneous changes which some 2+ times occur, besides controlling the patient at a satisfactory level of serum Ca [16. Calcium supplements are generally used, and it is essential that a regular diet must be fortified with at least 1 g/day of elemental calcium, preferably in 2-3 divided doses on an empty stomach to facilitate its increased absorption. There are now a wide variety of choices for treatment with vitamin D and/or its more active derivatives. Recently there has been widespread use of more active metabolites of vitamin D which include Calcidiol (25 hydroxy vitamin D, 25-200 fig/day) and Calcitriol (1,25 dihydoxy vitamin D, 0. These help in the increased mobilization 2+ of Ca from intestine and bone, particularly Calcitriol. The decision to treat hypocalcemic patients, further rests upon both the degree of hypocalcemia and the rate at which the condition develops. Chronic sialadenitis 131 A significant number of patients treated with I for carcinoma of thyroid often complain of symptoms like dryness of the mouth, pain in the parotid region, altered taste, and difficulty in 188 131 swallowing, poor oral hygiene and loss of appetite. Information regarding the effect of I on salivary glands, and the extent of damage produced is scanty. Quantitative parameters of salivary function using pertechnetate have been reported. The per cent uptake and excretion of TcO4 by the salivary glands in 131 controls (only thyrodectomized) and the I treated patients is shown in Table 16. Similarly, the per cent excretion of TcO4 by the salivary glands after sialogogue stimulation was significantly reduced (p <0. Reports indicate that chronic sialadenitis with xerostomia can occur in 12% of subjects. Reserpine has been used to protect glands, however, the benefits are doubtful [16. Radiation effects on gonads and fertility 131 One of the most dreaded and over exaggerated effects of I therapy has been the effect on the gonads. This is mainly because of the long term survival and the involvement of young individuals. However, reports of infertility are rare, despite the transient impairment of testicular germinal cell dysfunction [16. Long term follow-up of young males treated below the age of 21 years and followed for 19 years revealed 12% incidence of infertility which was not significantly different from that of the general population. To reduce gonadal irradiation it is advised that the patient should 131 drink plenty of water and void frequently for the first 72 hours after I administration. Ovarian function and fertility Female gonadal function and fertility has been documented in a few reports [16. Ten to 131 thirteen per cent of female children treated with I had a transient infertility for 3 and 14 years followed by a normal successful pregnancy. A more recent study from Italy showed no significant difference in the fertility rate and prematurity in a large series of 627 women 131 treated with I [16. Over the years data has been published on a large series of women 131 treated with I with no demonstrable effects on fertility or on the incidence of congenital abnormalities in children borne by these women (Table 16. Of the 91 children born, 68 were normal, 4 children died due to infectious diseases while no information was available in 5 children. A comparison with data published so far indicates that there is no significant effect 131 131 of I on the children born to parents treated with I therapy especially if an interval of 2 to 3 years has elapsed after treatment. In general the gonadal fear has been overstated and observation of thousands of patients treated all over the world reported no significant effects (Table 16. Chromosomal aberrations are known to occur at a higher 131 frequency after I treatment in peripheral lymphocytes of treated patients as compared to controls [16. There are only a few reports on pregnancy and foetal risks in patients treated 131 with I [16. In one series only one case of severe cardiac malformation among 73 new born children was observed. In this mother the calculated gonadal dose was not higher than in other mothers [16. It was presumed that high suppressive doses of thyroxin may have been an important factor in the low birth weight of neonates [16. The mild exogenous hyperthyroidism was probably responsible for the two spontaneous abortions which were recorded in this series. On the basis of the data it appears 131 irrational to dissuade young females treated with I from considering pregnancy. However, 131 pregnancy should be delayed for one to three years after the last I administration. Whether the effect is due to gonadal irradiation or to insufficient control of hormonal thyroid status 131 needs to be established. Overall the problems faced are not due to I but to the hormonal therapy which needs more stringent monitoring [16. Malignant neoplasm Induction of other malignant neoplasia and bone marrow damage are potentially more serious consequences. Incidence of bladder cancer has been reported slightly higher in these patients than seen in the general population [16. Sporadic cases of other malignancies like carcinoma of the breast, melanomas and others are also reported. The cancer patients are probably an increased risk of developing the second malignancies compared to general population rather 131 than a consequence of I therapy. The long survival time of patients would predispose them to development of another malignancy which occurs with the same frequency as those in an untreated population. Thirty one per cent presented with second concurrent malignancies at the time of treatment, while 41% developed a second malignancy after 5 or more years. External radiation treatment was given to more than half of them primarily as a mode of therapy for the second malignancy. It was suggested that an incidence of 5 per 1000 cases is more than expected in the 131 general population. Myelogenous leukaemia which occurs after I therapy occurs within 10 131 years of exposure. The chances of developing leukaemia are lower if the interval between I therapies is 12 months rather than a few months and if total doses are below 200 cGy to the blood. After constructing a careful decision matrix the conclusion was that the lifetime risk of 131 leukaemia is so small (<0. Whether 131 anaplasia sets in as a course of the natural history of the disease or following I therapy is 131 purely conjectural. Bone marrow suppression 131 Temporary marrow suppression is observed in patients treated with large dosages of I. When the mean blood radiation dose exceeds 267 rads (45-740 rads) about 20% patients had serious bone marrow suppression [16. However, studies at Memorial Hospital have not reported any temporary or permanent marrow suppression following the use of 75 mCi 131 (2. Effect of radioiodine therapy on renal system Radioiodine is excreted mainly through urine. This results in significant radiation exposure to the kidneys and bladder during therapy. To determine whether the radiation dose delivered to 131 the kidneys during I treatment caused any renal impairment, urinary albumin was used as an index. Microalbuminuria indicates slightly elevated urinary albumin excretion and is a marker for glomerular damage. Tubular dysfunction with impaired protein reabsorption may also play a minor role in the excretion of elevated urinary albumin. Hence, an elevation in 131 urinary albumin excretion after I treatment will predict radiation-induced renal damage if it occurred during therapy. Seventy-three patients were treated once, the remainder being treated two to six times. Scatter diagram relating the urinary albumin 131 concentration and cumulative activity of I administered. External X ray therapy given to patients with abdominal cancer can cause renal damage if the kidneys are included in the therapeutic field. They also stated that such therapy may lead to the development of acute or chronic radiation nephritis which causes proteinuria. Other complications of this therapy include benign or malignant hypertension and interstitial fibrosis. The renal tolerance dose for the external radiation therapy was 2300 cGy over 5 weeks and a dose of 2800 cGy or more delivered to both kidneys in 5 weeks or less would lead to renal failure. This is true in the case of intact thyroid gland, but where the thyroid tissue is not intact, the renal dose will be higher.
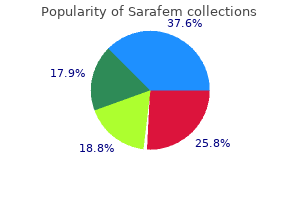
Stored Specimens and Ethical Concerns Most (75 percent) of the screening programs store the newborn dried blood specimens breast cancer metastasis to lung cheap sarafem 10mg on line, the length of time ranging from several months to as long as 25 years (McEwen breast cancer 3 day walk purchase sarafem cheap, Reilly breast cancer walk nyc purchase cheap sarafem on line, 1994) menstruation in space purchase sarafem 10mg overnight delivery. In virtually all of these instances women's health clinic ottawa riverside order 20 mg sarafem fast delivery, the retested result has been a marked increase in Phe rather than the normal result originally reported breast cancer knee high socks sarafem 10 mg amex, demonstrating laboratory error (Levy, 34 Albers, 2000). Stored specimens have also been used for metabolic research and to assess new technologies (Levy, Albers, 2000). The concerns include use of the specimens without consent to identify children with untreatable diseases, particularly those that might not be clinically expressed until many years later. Research in which the identity of the infant is removed from the stored specimen (anonymous studies) has generated much less controversy. The current issue of stored specimens, therefore, centers on control of their use and whether they should be used with retention of identifiers. Influence of phenylalanine intake on the chemistry and behavior of a phenylketonuric child. Rapid diagnosis of phenylketonuria by quantitative analysis for phenylalanine and tyrosine in neonatal blood spots by tandem mass spectrometry. Uber Ausscheidung von Phenylbrenztraubensaure in den Hann als Stoffwechselanomalie in Verbindung mit Imbezillitat. A simple phenylalanine method for detecting phenylketonuria in large populations of newborn infants. Descriptive epidemiology of missed cases of phenylketonuria and congenital hypothyroidism. Effective screening depends on smooth integration and appropriate timing of sample collection, laboratory testing, followup, diagnosis, treatment, and evaluation of outcome (American Academy of Pediatrics, 2000; Therrell, Panny, Davidson, et al. Universal screening systems are designed to respond to Federal and State mandates to provide all children with special needs, including those in traditionally underserved populations, with access to effective treatment. Procedures for establishing screening policy, providing laboratory services, and determining program rules and regulations vary. Some States suggest taking a repeat filter paper specimen on certain lower elevated levels, and others suggest that all elevations be referred for serum followup because false positives are infrequent and delays in diagnosis and treatment can affect outcome. Biopterin studies are also suggested by most screening programs, along with supplemental tests that may help in further diagnosis and nutritional management. Federal funding allows compensation for supplemental foods and formula as part of the Women, Infants, and Children program, or from Medicaid if the individual qualifies. Those ineligible for Federal funding do not always have access to third-party payers of the costs of food and formula required in all States. In self-employment insurance programs, payment decisions may rest with the employer (California Department of Health Services, 1997). Newborn screening: an overview of newborn screening programs in the United States, Canada, Puerto Rico, and the Virgin Islands. Over the past century, the world of biomedical science has enjoyed an exponential growth of technologies that now permit the molecular dissection of the human genome and the treatment of an expanding array of devastating genetic diseases. As the technological powers of health care have generated potential benefits, practitioners in medical genetics and genetics research have studied a plethora of ethical, legal, and social issues related to the applications and implications of new knowledge about hereditary health problems. At the interface of technology and its applications and implications are questions derived from concepts of personal autonomy, personal privacy, and confidentiality of genetic information. Also at this interface are concerns about making the new benefits available across the human population as a matter of public health. Out of these broad concerns have developed newborn screening programs that confer immense benefits to individuals, to families, and to society. The ethical principles of personal autonomy, personal privacy, and confidentiality of personal information now constitute the foundation of the practice of medicine. The principle of personal autonomy is understood as decisional privacy, or the right of an individual to make his or her own decisions, without duress or coercion, about which medical or other options to pursue. The concept of personal privacy protects individuals within the private sphere of the body so that others are constrained from touching or viewing the person inappropriately. Privacy of information includes respect for confidentiality of personal information that is exchanged within the professional-patient relationship, thus assuring candor in communication and resulting in accrual of benefits to the individual. Respect for these three facets of privacy is the basis of principles that govern the practice of medical genetics and genetic counseling. The doctrine of informed consent developed from principles of personal autonomy and personal privacy. One branch provided standards of conduct in the practice of medicine and surgery, and the other branch developed the principles of conduct in biomedical research. The principle of informed consent in the professional-patient relationship grew out of an expanded array of options that became available in medicine and surgery early in the 20th century. As patients became more aware of their options, they became quick to allege negligence when professionals failed to present all options that a patient might choose to pursue. The principle of informed consent in biomedical research grew out of numerous experimental regimes, carried out over the course of the 20th century, both in the United States and elsewhere, without the knowledge or consent of the individual subjects. Federal regulations also include special provisions for protecting vulnerable populations, including pregnant women, children, and prisoners. These principles now influence every aspect of the practice of medical genetics and genetic counseling and all phases of research in human and medical genetics. The advent of newborn screening for phenylketonuria in the 1960s ushered in the era of treatment for some infants who are born with devastating genetic diseases. Simple, reliable, inexpensive tests permit the early identification of serious genetic diseases that can then be managed for the benefit of the infant, in terms of normal, or nearly normal, development or health, and for the benefit of society, in terms of the public fisc. Several drops of blood samples are collected shortly after birth, blotted and dried on personally identified cards, and sent to screening laboratories for testing. Most States have legislated mandatory screening so that these samples can be gathered and tested without formal parental consent. Cards with surplus blood spots are retained, with identifiers, in laboratories for varying periods defined by State law. Debate over the past four decades about mandatory screening has weighed the negative invasion of privacy and parental autonomy against the positive benefits of screening, and all but two States have favored mandatory screening because of the immense benefits that are realized when infants are detected and treated early in life. Only two States require parental consent before samples are collected from the infant. Most States have loose provisions for telling parents about screening and for permitting parents to opt out for religious reasons. However, mandatory screening is so rigid in two other States that parents who refuse testing are subject to criminal penalties. The immense success of newborn screening programs reinforces and supports legislative decisions to screen for certain diseases without parental consent. Over the past decade, technical developments in molecular genetics have opened the door for vastly expanded research into the structure and function of countless genes. As the new technologies expand the power of research, genetics professionals have inquired about the possibility of using minute bits of dried blood from newborn screening samples to conduct research in medical and molecular genetics. The push to gain access to newborn screening samples has generated new debate about the appropriate use of samples that are collected without parental consent. Some professionals have noted that samples collected in the past were legally separated from the donors at the time of collection and should therefore be available to researchers on request. Others have carefully argued that these samples may be used for future research only after parents are recontacted for specific consent for specific research projects. Others have argued that these samples should be available to any researchers provided the samples are stripped of identifying information. The middle ground in using new collections of newborn screening tissue samples for present and future research may lie in establishing a protocol for mandatory screening, followed by a request for parental consent for future use of samples if the samples are likely to be sought for genetics research. The undeniable benefits of newborn screening justify continued mandatory programs so that parental consent for screening is not a critical factor. Decisions about future use in unspecified genetic research and tests should, however, rest with the donors of the samples or their parents. A short protocol of six simple, dichotomous questions could be presented to parents. These questions address the use of samples, with or without identifiers, with or without the option for being notified about the development of significant new information. The protocol 42 could provide for reciprocity or responsibility in following up on any new developments. This protocol protects families as the persons who may have a significant interest in future developments, and it also protects the researcher without imposing an undue burden. New technologies are expanding the interests of individuals, families, and genetics professionals. Achieving an acceptable balance among ethical principles and professional activities is a challenge that can be resolved by acknowledging that everyone has a stake in genetic information that is developed now and in the future. References American College of Medical Genetics Storage of Genetics Materials Committee. Response to National Bioethics Advisory Commission on the ethical issues and policy concerns surrounding research using human biological materials. Approximately one-half of the patients were younger than 12 years of age, and 93 percent of these were on a phenylalanine (Phe)-restricted diet. Of those patients 12 years of age and older, 54 percent were on a Phe-restricted diet. The survey instrument included questions about diagnosis, initiation of treatment, assessment of biochemical control, and continuation of dietary restriction. Some 99 percent of the clinics prescribed a restricted diet for life for males; 85 percent prescribed a restricted diet for life for females. These practices had been in place for more than 7 years at 54 of the 87 clinics (62 percent), and for more than 3 years at 10 of the 87 (11 percent). Monitoring Intervals After Instituting a Phe-Restricted Diet Monitoring consisted of measurement of Phe concentration in a blood sample, collected at most centers from patients after they had fasted overnight. A majority of the clinics (41 of the 87, or 47 percent) used the McCaman-Robins fluorometric method. Time Between Testing and Notification the amount of time between obtaining blood from patients and reporting the results to the family varied from 1 to 10 days. Most clinics reported the results within 1 to 3 days (52 of the 87, or 60 percent). Other deficiencies involve factors related to compliance with a restricted diet, such as how to design a more palatable diet. Outcome of treatment in young adults with phenylketonuria detected by routine neonatal screening between 1964 and 1971. Phenylketonuria: current dietary treatment practices in the United States and Canada. Long-term follow-up of children with classical phenylketonuria after diet discontinuation: a review. Long-term followup of patients with classical phenylketonuria after diet relaxation at 5 years of age. Development of guidelines for treatment of children with phenylketonuria: report of a meeting at the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development held August 15, 1995, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland. Biochemical control, genetic analysis and magnetic resonance imaging in patients with phenylketonuria. Management of phenylketonuria for optimal outcome: a review of guidelines for phenylketonuria management and a report of surveys of parents, patients, and clinic directors. Phase B investigated diet continuation versus discontinuation after the age of 6 years. The study designs for both investigations have been published (Williamson, Dobson, Koch, 1977; Koch, Azen, Friedman, et al. The Phe-restricted diet was based on Lofenelac, a casein hydrolysate, and was designed to provide a balance of nutrients with adequate protein, calories, and other essential amino nutrients. Blood Phe levels were measured weekly during the first year and monthly thereafter. Other summary measures included rate of rise in blood Phe levels above 900 mmol/L through 6 years of age (Williamson, Koch, Azen, et al. The subjects were predominantly Caucasian (96 percent); 43 percent were first-born, and 57 percent were male. Of the mothers, 16 percent were younger than 20 years of age at the birth of the child. The children in this sample exhibited an overall prevalence of congenital anomalies (9. Annual assessments of height, weight, and head circumference through 4 years of age compared favorably with national norms (Holm, Kronmal, Williamson, et al. Higher serum Phe levels were found to be positively correlated with weight, particularly for girls (p<. A followup report on the subjects confirmed these findings at 12 years of age (Azen, Koch, Friedman, et al.
Syndromes
- Overactive reflexes
- Antibiotics
- Name of the product (ingredients and strengths, if known)
- Health history
- Infections the mother passes to her baby in the womb (such as toxoplasmosis, rubella, or herpes)
- Take part in activities that distract from the itching during the day and make you tired enough to sleep at night.
There is a false negative rate for benign (Thy2) cytology results (usually less than 3% breast cancer 49er hats order line sarafem. Adenomatoid nodules are the main cause for discrepant histology in 234 thyroid fine-needle aspirates reported as follicular neoplasm Diagnostic Cytopathology 2012;40:375-379 pregnancy 9 weeks cramping buy cheap sarafem 20 mg online. The triage efficacy of fine needle aspiration biopsy for follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma using the Bethesda reporting guidelines menopause 53 years old generic 10 mg sarafem overnight delivery. Factors affecting inadequate sampling of ultrasound- guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid nodules women's health clinic st louis buy discount sarafem 10 mg on-line. Comparison of palpation-guided versus ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsies of thyroid nodules in an outpatient endocrinology practice womens health network reviews discount sarafem 20 mg online. Nomogram for predicting malignancy in thyroid nodules using clinical menstrual flow is actually sloughed off purchase sarafem toronto, biochemical, ultrasonographic, and cytologic features. New guidelines for the management of thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration cytology in the diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules. Rapid onsite evaluation improves the adequacy of fine-needle aspiration for thyroid lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Optimal indication of thyroglobulin measurement in fine- needle aspiration for detecting lateral metastatic lymph nodes in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Does routine consultation of thyroid fine-needle aspiration cytology change surgical managementfi Effect of the Bethesda system for reporting thyroid cytopathology on thyroidectomy rates and malignancy risk in cytologically indeterminate lesions Surgery 2010;148:1267-1272. Malignancy risk for fine-needle aspiration of thyroid lesions according to the Bethesda System for reporting thyroid cytopathology. Comparison of malignancy rate in thyroid nodules with cytology of indeterminate follicular or indeterminate hurthle cell neoplasm. A large multicenter correlation study of thyroid nodule cytopathology and histopathology. How to combine ultrasound and cytological information in decision making about thyroid nodules. Interobserver variability amongst cytopathologists and histopathologists in the diagnosis of neoplastic follicular patterned lesions of thyroid. Prevalence and prediction of malignancy in cytologically indeterminate thyroid nodules. Fine needle aspiration cytology of the thyroid: a comparison of 5469 cytological and final histological diagnoses. Improving prediction of malignancy of cytologically indeterminate thyroid nodules. Clinical significance of distinguishing between follicular lesion and follicular neoplasm in thyroid fine-needle aspiration biopsy. If there are progressive/severe respiratory problems associated with a thyroid mass, patients must be referred and seen without delay. Decisions should be made promptly with respect to diagnosis and treatment (maximum 31 days from diagnosis to first treatment and 62 days from urgent referral to first treatment (Chapter 3, Figure 3. Measurement of Tg in aspirate washout fluid may aid the diagnosis of lymph node metastasis (Appendix 1. Additional written or audio-visual material are recommended (Appendix 5, Patient Information Leaflet 9 3), but are not a replacement for verbal consent (4, D). In patients with suspected or proven thyroid cancer, assessment of vocal cord function 13 is recommended prior to surgery for diagnostic and audit purposes (2++, B). In expert centres, nerve injury rates are no higher after re-operative central neck node 14, 15 16-19 dissection surgery or for recurrent thyroid cancer. Infiltration by tumour contributes to recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy rates in malignant disease. Attempts should be made to identify / protect preserve the external branch of the 13 superior laryngeal nerves by ligation of the superior thyroid vessels at the capsule of the gland. External laryngeal nerve injury has an associated morbidity, particularly in voice-quality changes. Total thyroidectomy for large tumours or tumours of any size with additional risk factors has 23, 24 been shown to be associated with fewer recurrences and better survival. Total thyroidectomy is recommended for patients with tumours greater than 4 cm in diameter, or tumours of any size in association with any of the following characteristics: multifocal disease, bilateral disease, extra-thyroidal spread (pT3 and pT4a), familial disease, and those with clinically or radiologically involved nodes and / or distant metastases (2-, D). The potential benefits of prophylactic surgery should also be judged in the context of potential for increased morbidity associated with the injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerves and parathyroid glands. Male gender has previously been considered as an additional risk factor for reduced disease- specific survival, but two recent studies have failed to confirm that it is an independent risk 48, 49 factor for survival. There is uncertainty as to whether a sole finding of microscopic extra- 50, 51 thyroidal extension (pT3) is an adverse risk factor. The addition of unilateral central neck dissection to total thyroidectomy compared with total thyroidectomy, alone does not result in 44 lower Tg concentrations at 6 months post ablation. Those against, state there is no evidence to indicate that prophylactic lateral neck dissection improves survival or loco regional control and over-treats 75% of 43 patients. Prophylactic lateral neck dissection in patients with no evidence of central compartment lymph node metastases, is not recommended (2+, C). If definitive histology reveals a follicular adenoma or a hyperplastic nodule, no further treatment is required. Patients with tumours <4 cm, in the absence of other adverse risk factors (age > 45 years, widely invasive, lymph node / distant metastases, angioinvasion) appear to 70-72 have an excellent prognosis. Lymph node metastases are reported to occur in 3%-25% of 78 cases, tumour size (> 5cm) and older age (> 80 years) are risk factors for nodal disease. Loco regional recurrence of Hurthle cell carcinoma is not associated with lymphoid tissue and most likely to result from spread via 80 venous channels. The evidence for an advantage of prophylactic neck dissection compared to no prophylactic neck dissection, in patients with Hurthle cell carcinomas is unclear. In patients with bilateral disease it may not be possible to remove the entire tumour without damaging both recurrent laryngeal nerves. A small residue of tumour may be left behind to protect the nerve on one or both sides (4, D). In individual patients with locally advanced disease involving the upper aero- digestive tract, curative resection of the tracheal wall and/or oesophagus should be 83, 84 considered (2-, C). It is recommended that patients with voice change after thyroidectomy, undergo 13 laryngoscopy (Chapter 11. Expert opinion recommends routine post-operative laryngoscopy in patients who have 13 undergone thyroidectomy (4, D). A baseline postoperative serum Tg should be checked, preferably no earlier than 6 weeks after surgery (Appendix 1) (4, D). Preoperative diagnosis of cervical metastatic lymph nodes in papillary thyroid carcinoma: comparison of ultrasound, computed tomography, and combined ultrasound with computed tomography. Efficacy and safety of central compartment neck dissection for recurrent thyroid carcinoma. Importance of the intraoperative identification of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve during thyroidectomy: electromyographic evaluation. Papillary thyroid carcinoma: 35-year outcome and prognostic factors in 1858 patients. Influence of previous radiation exposure on pathologic features and clinical outcome in patients with thyroid cancer. Prognostic relevance of previous exposure to ionizing radiation in well-differentiated thyroid cancer. Clinical behavior of radiation-induced thyroid cancer: factors related to recurrence. Extent of thyroidectomy is not a major determinant of survival in low- or high-risk papillary thyroid cancer. Matsuzu K, Sugino K, Masudo K, Nagahama M, Kitagawa W, Shibuya H, Ohkuwa K, Uruno T, Suzuki A, Magoshi S, Akaishi J, Masaki C, Kawano M, Suganuma N, Rino Y, Masuda M, Kameyama K, Takami H, Ito K. Thyroid Lobectomy for Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Long-term Follow-up Study of 1,088 Cases. Population-based study evaluating and predicting the probability of death resulting from thyroid cancer and other causes among patients with thyroid cancer. Optimization of staging of the neck with prophylactic central and lateral neck dissection for papillary thyroid carcinoma. Impact of routine unilateral central neck dissection on preablative and postablative stimulated thyroglobulin levels after total thyroidectomy in papillary thyroid carcinoma. A Meta-analysis of the Effect of Prophylactic Central Compartment Neck Dissection on Locoregional Recurrence Rates in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer. Sex is not an independent risk factor for survival in differentiated thyroid cancer. Extrathyroidal extension is not all equal: Implications of macroscopic versus microscopic extent in papillary thyroid carcinoma. American Thyroid Association consensus review and statement regarding the anatomy, terminology, and rationale for lateral neck dissection in differentiated thyroid cancer. Nodal recurrence in the lateral neck after total thyroidectomy with prophylactic central neck dissection for papillary thyroid cancer. Performing contralateral central lymph node dissection in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a decision approach. Pathological definition and clinical significance of vascular invasion in thyroid carcinomas of follicular epithelial derivation. Can Minimally Invasive Follicular Thyroid Cancer be Approached as a Benign Lesionfi Does hurthle cell carcinoma of the thyroid have a poorer prognosis than ordinary follicular thyroid carcinomafi Comparison of clinical characteristics at diagnosis and during follow-up in 118 patients with Hurthle cell or follicular thyroid cancer. Patients with follicular and Hurthle cell microcarcinomas have compromised survival: A population level study of 22,738 patients. Histological patterns of locoregional recurrence in Hurthle cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland. True vocal fold immobility in the setting of well- differentiated thyroid carcinoma: unusual illustrative cases and recommendations for operative strategy. Should an Involved but Functioning Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve be Shaved or Resected in a Locally Advanced Papillary Thyroid Carcinomafi Fine needle aspiration cytology of primary lymphoma of the thyroid: a report of 17 cases. Consensus statement on the terminology and classification of central neck dissection for thyroid cancer. If a total thyroidectomy is not carried out, the surgeon should document the exact extent of surgery to each lobe (4, D). Level V Posterior triangle nodes (anterior border is posterior border of sternomastoid, posterior border is anterior border of trapezius) subdivided into Va and Vb. Extended neck dissection is defined as removal of one or more additional lymph node groups such as parapharyngeal, superior mediastinal and paratracheal nodes and/or non-lymphatic structures (digastric muscle, skin). Microcarcinomas constitute approximately 30% of all differentiated thyroid cancers and are largely responsible for the rise in incidence of thyroid cancer seen in many 1 countries over the past decade. Distant metastases are documented in 0-3% cases at diagnosis However, lymph node involvement, is relatively common at 12. Mortality 31,22,32,33,34,35,11 the mortality is very low with either no deaths or only occasional deaths 13,14,15,16,17,18, 36,26,37,38,39,40 reported, ranging between 0. Distant metastases the risk of new distant metastases among 4,096 patients from 15 pooled studies with a 41 median follow-up between 3. The risk of locoregional recurrence among 5,256 patients from 16 pooled studies with a median follow- 41 up between 3. Recurrences were amenable to successful treatment in most cases and 26 did not adversely affect survival. Given that long-term survival is nearly 100%, the objective of any treatment is to reduce the risk of locoregional recurrence (2. Given that for the general population the lifetime risk of 48 developing any cancer is about 33% and the risk of dying from any cancer 28% the benefits of screening for recurrence, are unlikely to outweigh the disadvantages. The risk of developing hypothyroidism after thyroid lobectomy can be 15% or 49,50,51 higher, therefore annual biochemical surveillance in primary care is 52 recommended (4, D). Incidental thyroid carcinoma in a large series of consecutive patients operated on for benign thyroid disease. Incidence and histopathological behavior of papillary microcarcinomas: study of 429 cases. Incidental occult carcinomas in total thyroidectomy for benign diseases of the thyroid. What is the biology and optimal treatment for papillary microcarcinoma of the thyroidfi Incidental papillary microcarcinoma of the thyroid-factors affecting lymph node metastasis. Papillary microcarcinoma of the thyroid: predicting factors of lateral neck node metastasis. Clinical and histological characteristics of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: results of a retrospective study in 243 patients.
Discount sarafem online visa. Practice Yoga Like Jennifer Aniston from Women's Health.
References
- Carrasco R, Pascual JM, Reina T, et al. Chordoid glioma of the third ventricle attached to the optic chiasm. Successful removal through a trans-lamina terminalis approach. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2008; 110:828-833.
- Heim-Duthoy KL, Chitwood KK, Tortorice KL, et al. Elective cyclospori-e withdrawal 1 year after re-al tra-spla-tatio-. Am J Kid-ey Dis. 1994;24(5):846-853.
- Stallmeyer B, Drugeon G, Reiss J, et al. Human molybdopterin synthase gene: identification of a bicistronic transcript with overlapping reading frames. Am J Hum Genet 1999;64:698.
- Gudena V, Verma N, Post G, et al. Metastatic chest wall malignant schwannoma responding to sorafenib: case report and literature review. Cancer Biol Ther 2008;7(6):810-813.
- Journal of Clinical Oncology 16:1310-1317.